Over the previous few years, we’ve been studying how one can adapt our layouts to the infinite canvas of the net. Our websites will be considered on any dimension display screen, at any time, and responsive design is one method that lets us accommodate the net’s variable form. However with the entire challenges we’re going through and people but to come back, we have to start constructing not simply patterns, however ideas for responsive design—ideas that can enable us to focus not simply on format, however on the standard of our work.
Article Continues Under
If every a part of your responsive interface is kind of self-contained—with its personal format guidelines, content material wants, and breakpoints—then the code behind every component’s design is much much less essential than pondering fastidiously about how and why a component ought to adapt. In different phrases, how will we transfer past pondering by way of columns and rows, and begin speaking in regards to the high quality of our responsive designs? And what would frameworks to assist that appear like?
Truthfully, there’s no good reply to that query. However just lately, quite a lot of designers and organizations have began sharing the vocabulary they use to resolve how and when their responsive designs ought to adapt. Vox Media, for instance, thinks of their content material as present inside a river—and in line with the metaphor, the circulation of that content material will be interrupted at sure factors. Right here’s how they describe the entrance pages of Vox.com:
Content material flows round “rocks” and “breakers,” that are modules resembling a “Most Commented” listing or a row of “Fashionable Movies.” Many of those behaviors stay within the new format system, however the important thing distinction is an added contextual layer. Parts within the river are laid out to higher spotlight the range of content material on Vox—articles, options, movies, editorial apps, card stacks, to call just a few. Each shows in another way relying on its kind and neighboring entries.
Word that the language they use to speak in regards to the high quality of their layouts doesn’t revolve round columns or rows. There’s nary a point out of grids. For Vox, the design course of begins with content material precedence and evolves right into a format. By understanding the load and significance of every piece of content material that flows by the river, the Vox group can algorithmically generate a responsive format that greatest displays the significance of the data inside it.
Beginning with an summary system of columns and rows can be mistaken for them—and, I’d argue, for each internet designer. In any case, in response to Mark Boulton, there are three elementary advantages of a grid system:
- Grid methods create connectedness. A well-made grid can visually join associated items of content material or, simply as importantly, separate unrelated components from one another. In different phrases, they assist us create narratives from our format.
- By establishing predefined alignment factors, grid methods assist designers resolve format issues.
- A well-designed grid system will present visible pathways for the reader’s eye to comply with, and permit them to higher perceive a visible hierarchy.
As Boulton notes, we traditionally created grid methods by adopting a “canvas in” technique. Working from the perimeters of a printed web page, designers would subdivide a web page right into a system of columns and rows, and place photographs and textual content upon that grid in pleasing, rational preparations. However the internet doesn’t have any such boundary—in spite of everything, it’s the primary actually fluid design medium. Consequently, Boulton argues we should always as a substitute undertake a “content material out” method to designing our grids: to construct extra advanced format methods out from a basis of small, modular items of content material. And to take action, Boulton proposes three guiding ideas:
- Outline relationships out of your content material. A grid for the net needs to be outlined by the content material, not the sting of an imaginary web page.
- Use ratios or relational measurements above mounted measurements.
- Bind the content material to the machine. Use CSS media queries, and strategies resembling responsive internet design, to create layouts that reply to the viewport.
By understanding the form of our content material, we will create versatile layouts that assist connectedness—not simply between associated items of data, however between our layouts and the machine. We are able to make responsive grid methods that don’t simply match on an ever-increasing variety of screens—they’ll really feel at residence, wherever they’re considered.
Ideas are great, in fact, however we nonetheless must discover a technique of implementing them: of translating these beliefs into sensible responsive patterns and layouts. For me, that “content material out” course of begins by trying on the smallest model of a chunk of content material, then increasing that component till its seams start to point out and it begins to lose its form. As soon as that occurs, that’s a chance to make a change—to introduce a breakpoint that reshapes the component and preserves its integrity.
However first, we want a technique of discovering a component’s seams, and understanding the way it loses its form. For me, that course of begins by taking a look at 4 traits: width, hierarchy, interplay, and density.
Width#section4
Width may be a bit of self-evident. Because the width of a viewport adjustments, so does the width of a responsive design. However because the design will get wider or narrower, so will the weather inside it, and as these modules develop or contract, there could also be alternatives so as to add a breakpoint.
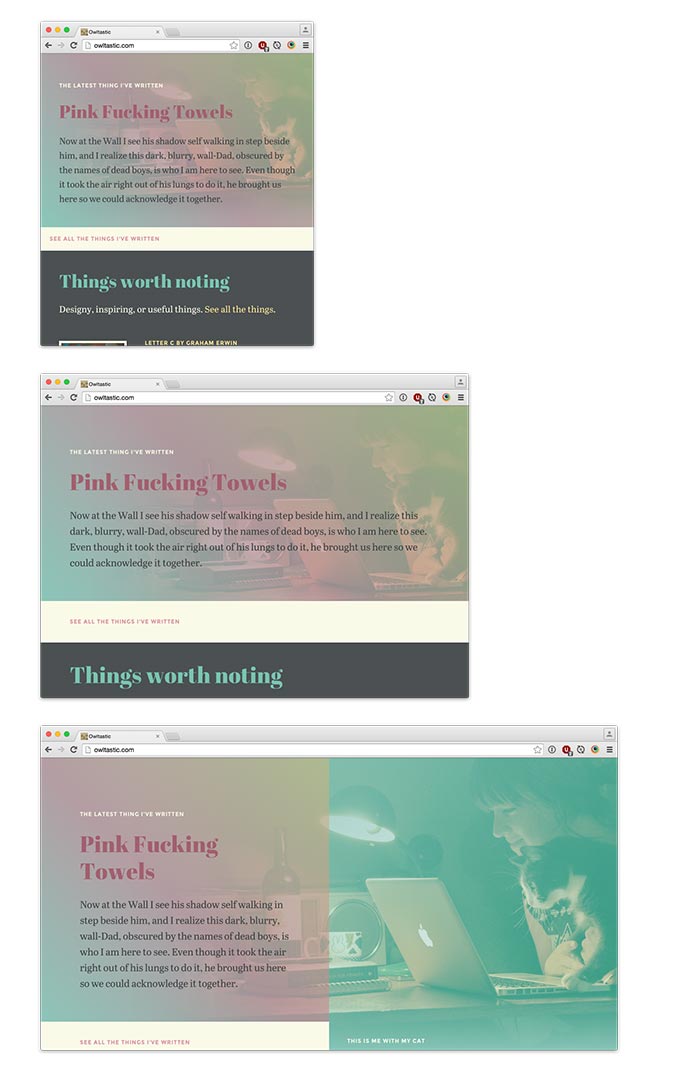
Hierarchy#section5
Width is, I’m positive you’ll agree, the most typical attribute of a responsive design—but it surely’s not the one one. As the form of a component adjustments, the hierarchy of components might have to vary as nicely.
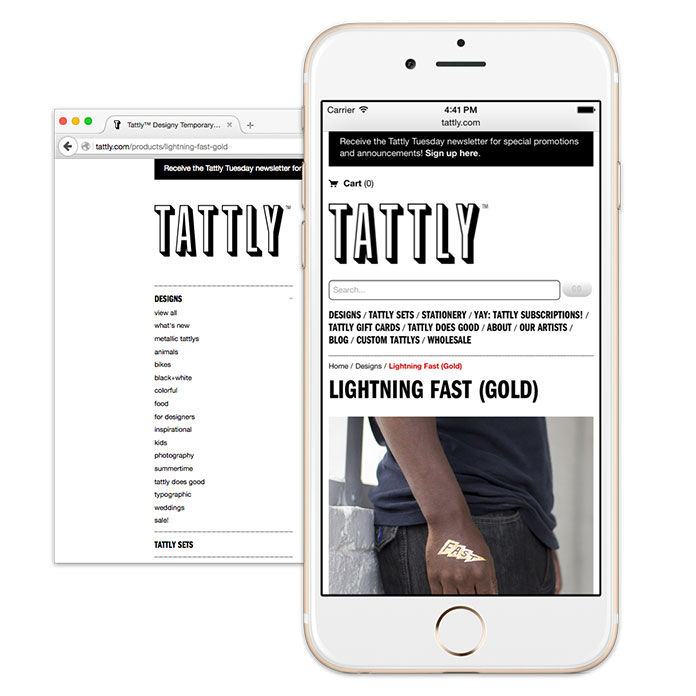
Let’s take a fast take a look at a product web page on Tattly’s responsive ecommerce web site. When considered on wider screens, the first content material space has two key items of data: a photograph carousel of the product on the left, and a name to motion to buy the product on the fitting.
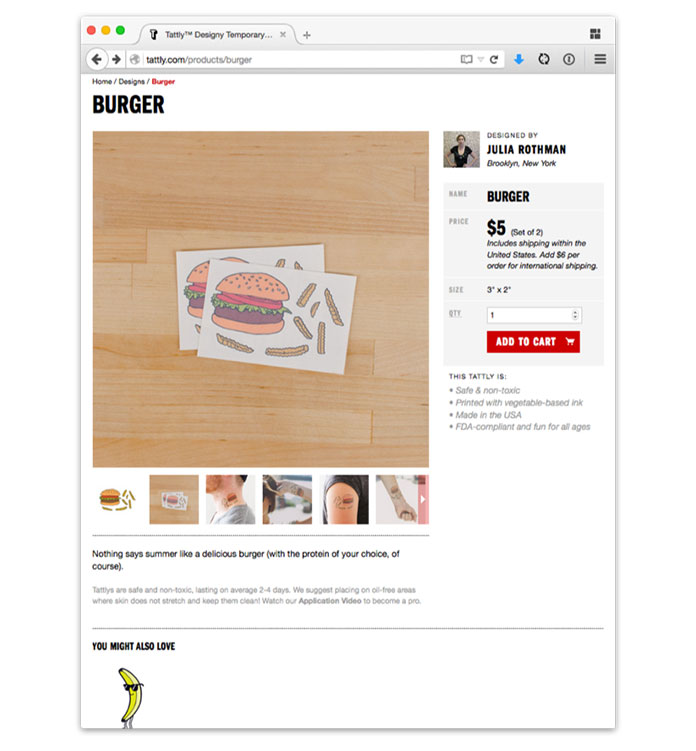
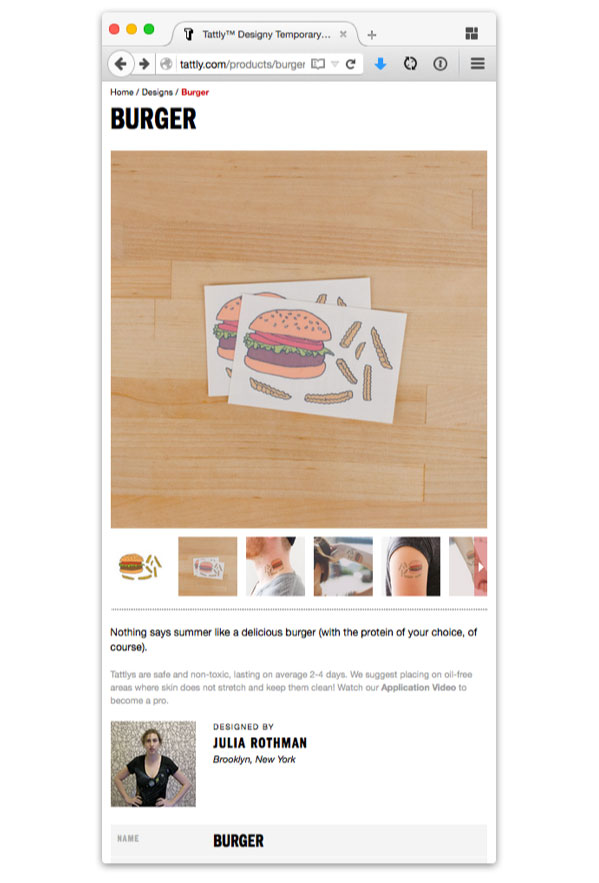
However that’s only one view of this specific a part of the design, as a result of as screens get narrower, we lose the flexibility to put a number of columns facet by facet. That’s the place a query of hierarchy arises: in a single-column format, which piece of content material ought to seem first? Tattly opted, fairly rightly, to guide with pictures of the product—however you could reply hierarchy questions in another way in your web site.
Hierarchy is mostly a reminder to be extra vertically conscious in our designs. In any case, now we have min-width and max-width media queries, however can even avail ourselves of min-height and max-height queries extra usually. I believe the navigation thực đơn for the Subject Museum superbly balances vertical and horizontal layouts.
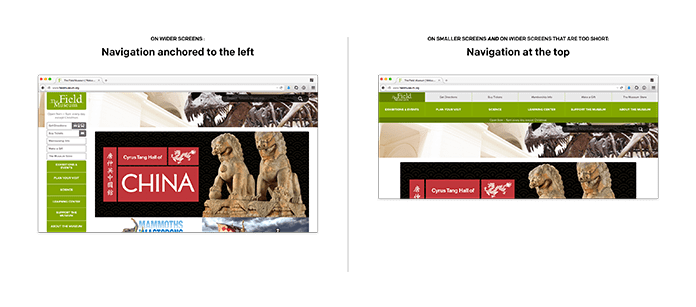
On wider screens, the navigation is anchored to the left fringe of the design, and spans the complete top of the viewport. You might discover that they’re utilizing the versatile field mannequin, or flexbox, a complicated CSS format technique we’ll take a look at later on this chapter. However since flexbox permits components to routinely fill the house accessible to them, because the thực đơn will get taller or shorter, the navigation components resize vertically—however under a sure width or top, the thực đơn is positioned on the prime of the web page.
By minding the navigation’s vertical edges, the Subject Museum was capable of introduce alternate layouts to make sure the content material inside their navigation thực đơn was by no means hid, obscured, or clipped. In different phrases, the breakpoints we introduce to our responsive designs aren’t tied to the form of a tool’s display screen. As a substitute, our media queries defend the integrity of the content material we’re designing.
Interplay#section6
The way in which we work together with a component could change together with the design. Responsive navigation methods are in all probability the obvious instance of this. As we noticed in Chapter 2, menus are sometimes displayed in full at wider breakpoints however hid at smaller ones, maybe hidden behind expandable icons or hyperlinks when house is at a premium.
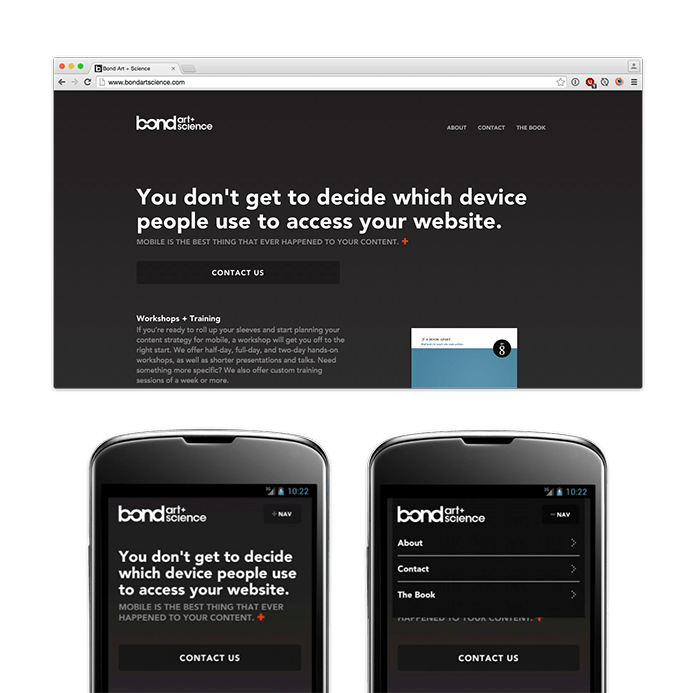
However navigation isn’t the one form of content material that may require interplay adjustments. For instance, take the responsive sports activities brackets designed by SB Nation. Whereas they seem as complex-looking charts at wider breakpoints, an easier, extra linear view of the brackets is proven on smaller screens.

Together with the simplified format, the brackets are offered as carousels within the smaller view, the place actual property is extra expensive. Every of the 4 areas for the bracket are a single slide within the carousel, permitting the consumer to cycle by for particulars. The knowledge in each visible states is identical, however the interplay mannequin adjustments.
Density#section7
Lastly, the quantity of data you’re displaying in a component would possibly must fluctuate over time—in different phrases, the density of data can change. The Guardian’s characteristic on the 2015 Oscars is filled with examples of this, with responsively designed timelines displaying a major quantity of film information. Above a sure width, thumbnail photographs are loaded in, barely rising the visible (and informational) density of the timeline.
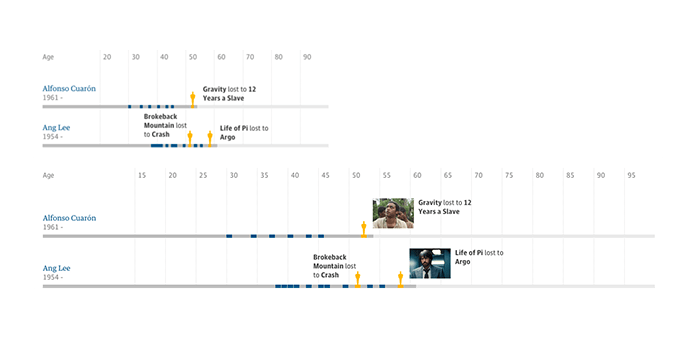
Density is, as you might need guessed, an space the place you need to tread very fastidiously. As we’ve mentioned earlier than, eradicating or hiding info as a result of it doesn’t match will be problematic.
Personally, I believe the Guardian’s timelines work so nicely as a result of the pictures proven at wider breakpoints are enhancements: they’re not vital to understanding the data round them. May they’ve designed alternate variations of the timelines to point out photographs in any respect breakpoints? Presumably. However I believe this can be a great instance of density used to lighten the visible influence of a design, eradicating extraneous info with out impeding entry to the content material.