Twelve years in the past, John Allsopp requested us to embrace the adaptable nature of the net. We didn’t hear.
Article Continues Under
Though the net requirements motion that adopted advocated the separation of presentation and content material—a vital requirement for adaptive design—this solely manifested itself in code. Floated divs changed desk cells, but layouts remained ruled by the rigid conventions of print.
At present, when each system begs to be linked, it has grow to be simpler—nearly essential—to just accept the adaptable nature of the net. Responsive internet design is an rising finest apply, and our layouts have gotten extra versatile. However as soon as once more, innovation is concentrated on technical implementations whereas the visible aesthetic stays ignored.
To place it one other means, we’re embracing “responsive” however neglecting the second half: “design.” We’re changing fixed-width divs with fluid ones. As we bear a interval of reassessment, each of our apply and of our instruments, now’s the proper time to hunt out an aesthetic that’s more true to the medium.
The fabric of the net#section2
To correctly design for a medium, you have to perceive it. I like to think about the net as a sort of materials, with distinctive traits we will reap the benefits of, and limits it may possibly attain earlier than it breaks. The net may nearly be thought of a composite, made up of HTTP (the how), URLs (the the place), and HTML (the what). Omit any one in all these elements and also you’re now not constructing the net.
It’s this mixture of protocols and conventions that helps the net obtain what Sir Tim Berners-Lee calls its “main design precept”: universality.
It ought to be accessible from any sort of {hardware} that may connect with the web: stationary or cell, small display or giant.
With universality so inherent to the medium, it might be mentioned that the net is responsive by default. “Responsive” isn’t a lot a method or course of, however a basic attribute of the platform—and it’s one we threaten with every line of CSS and JavaScript we lay upon it. Universality transcends visible design, too: Web sites should be simply as straightforward to make use of when displayed as plain textual content or learn out loud.
This nature, and these traits, ought to inform each side of our design. So how may the overriding aesthetic of the net change had been we to design with this common nature in thoughts?
The medium is the message#section3
Like the net, tv is a medium the place the entry units differ: Televisions can range in dimension, decision, side ratio, and refresh charge.
This was very true within the Nineteen Seventies and early Nineteen Eighties. Though packages had been recorded in coloration, broadcasters nonetheless needed to think about the massive quantity of people that owned black-and-white units. On-screen graphics wanted to work on each sorts of screens, so designers used contrasting shapes and colours. For instance, the idents for BBC1 used a yellow (and later, brilliant inexperienced) rotating globe on a darkish blue area. The ensuing design might have been garish, however it labored.


Tv is going through one other interval of transition, this time towards a high-definition widescreen format. As a result of many viewers personal standard-definition 4:3 televisions, designers once more must compromise, working inside a “secure space” to make sure graphics don’t get cropped on older units. As such, graphics on widescreen televisions are likely to float in the midst of the display, not but capable of make use of the total width.
The overriding aesthetic of tv will proceed to alter, however it should stay ruled by advances in know-how and designers’ understanding of its limitations.
Every part outdated is new once more#section4
Earlier than “killer web sites” and the need to supply print-like layouts—when bandwidth was restricted and small screens may solely show 256 colours—pixel graphics had been thought of de rigueur. Layouts had been easy and centered.
In 1995, Hotwired used simply sixteen colours. Navigation on the homepage consisted of little greater than six four-color, 1kb GIFs representing every subject space. The structure was simply these pictures, centered:
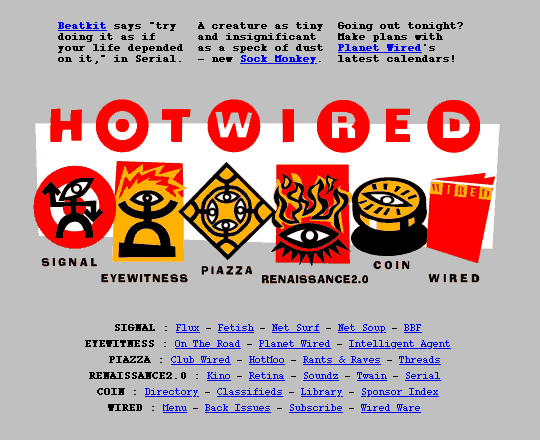
Hotwired, circa 1995
Surrounded by high-resolution shows and limitless bandwidth, it’s straightforward to overlook that comparable constraints nonetheless exist. Though units have gotten ever extra highly effective and feature-rich, much less succesful units proceed to be developed as properly; for instance, the Amazon Kindle is a well-liked system, but many of the line’s e-reader fashions function mobile connectivity and a monochrome E Ink show.
Embracing constraints#section5
Within the transfer to adaptive layouts, one other constraint has revealed itself: Bitmap pictures fail to reply, be it to the dimensions of the viewport or to out there bandwidth.
This isn’t a failing of the net; that we will embed various kinds of media right into a webpage is a helpful function. However not all codecs share the net’s traits. There’s an incredible alternative to develop a responsive bitmap format, and I doubt pictures will really really feel a part of the net till such a factor exists. Within the meantime, the query persists: How can we make extremely detailed photographic pictures work inside such an adaptable medium?
Many have tried to reply this query with technical options. Since advanced and fragile hacks had been discovered wanting, efforts have moved to defining new requirements, with a consensus forming round those who detect when in another way sized variations of a picture ought to be requested and displayed.
It’s within the realm of constraint that creativity is fostered. Designers have but to push in opposition to the bounds of what’s attainable. In looking for design options to this drawback, we may create an aesthetic extra applicable to the medium—and maybe understand that the responsive picture drawback solely exists as a result of our design conventions stay rooted in print.
With out such a interval of experimentation and reflection, I concern we may truly introduce requirements that go in opposition to the medium’s universality; modern-day <font> components nearly.
Designing round the issue#section6
Fortunately, builders and designers are beginning to undertake such experimentation, and are discovering options that negate the necessity for brand new requirements.
1. Optimization#section7
Fairly than producing in another way sized pictures and figuring out which ought to be proven, an alternative choice is to serve a single, extremely optimized picture as an alternative.
The dConstruct Archive is a small website the place individuals can hearken to talks given at earlier dConstruct conferences. Right here, background element across the face of every speaker has been blurred out, producing pictures with fewer compression artifacts and subsequently smaller file sizes. This method works particularly properly for portraits, as people are likely to deal with facial options anyway.


To work out which picture sizes to make use of, the smallest and largest shows had been taken into tài khoản. We will already see a failing in present responsive picture proposals. For those who go to this website, you’ll discover that bigger viewports typically show smaller pictures, as a result of the dimensions of the picture required is commonly depending on the dimensions of its containing block, not the dimensions of the viewport. But viewport is the worth the proposed requirements would have us question.
2. Altering the aesthetic#section8
If pictures with fewer colours and better ranges of compression can ship smaller information, then maybe our designs ought to mirror this.
With a theme of “enjoying with the long run,” the dConstruct 2012 convention website employed a extremely typographic design that featured monochrome pictures with areas of flat coloration. This design choice meant pictures might be actually small, some needing as few as eight colours:


As we noticed within the tv instance, the constraints of a medium can impression the ensuing aesthetic. In that case, ought to pictures with fewer colours or blurred backgrounds—and even perhaps noticeable compression artifacts—grow to be an accepted norm on the internet? Certainly the recognition of companies like Instagram (itself a product born of constraints) has confirmed that pictures is judged by its content material, not by its decision.
3. Progressive enhancement#section9
Altering the visible aesthetic to go well with the wants of the medium is a fantastic splendid, however it’s unlikely to be accepted by some shoppers, and let’s face it: It’s not at all times applicable. In reality, it appears we hardly ever ask that query: What is acceptable? By evaluating our content material, we will determine what number of pictures are literally required to convey a message.
Fairly than growing the decision of pictures as websites scale up, we will take into consideration growing their quantity as an alternative. This ties in properly with the concepts round progressive enhancement: offering a baseline expertise that’s enhanced as system functionality improves.
The BBC Information cell website is a good instance of progressive enhancement. The uncooked HTML supply references simply two pictures: the BBC emblem, and a picture for the principle story. Each system receives this, and pages can weigh as little as 28kb—fairly a feat on this planet of 5Mb web sites.
When accessed on extra highly effective units like newer smartphones, tablets, and desktop computer systems (these that may “lower the mustard“), a picture is displayed for every story. These pictures have been deemed “good to have”—enhancements to the core expertise which might be conditionally requested after the essential web page has loaded.

Progressive enhancement has lengthy featured within the developer’s toolbox, however it ought to now function all through the design course of. By serious about web sites in much less binary phrases (desktop versus cell; IE6 versus “trendy” browsers), we will create experiences that adapt to the various panorama of the net.
Adapting our assumptions (not simply our layouts)#section10
Think about the design of a brand new web site. Do you see a structure framed by a header and footer, with navigation operating alongside the highest and a most important content material space that includes a sidebar?
We have to reset such assumptions.
Fairly than search inspiration from print, maybe we should always look extra towards software program design. Desktop functions have lengthy been imitated on the internet, notably for productiveness functions, and they’re typically unbearable because of this. Extra profitable interfaces mix the perfect facets of desktop functions with the native interface of the net—suppose Gmail versus Yahoo! Mail.
Comparable pondering is now being dropped at content-focused functions, largely because of the introduction of the Chrome Net Retailer in 2010. This function gave Chrome builders a market to promote and promote apps constructed utilizing internet requirements, and lots of have created apps that repurpose content material out there on the internet.
That these apps can solely be seen utilizing Chrome is an unnerving requirement, and one worthy of protest. However, if we have a look at these apps from a purely visible standpoint and evaluate them to their conventional web site counterparts, we’ll see {that a} clean canvas eliminated of assumptions can ship experiences extra relevant to the net.
Solely the information that’s match to print#section11
Once we consider web sites impressed by print, these of newspapers spring to thoughts. The web site for The New York Occasions encompasses a fastened, densely packed, multi-column grid. Like many up to date websites, content material is suffocated by promoting, sharing widgets, and associated hyperlinks:
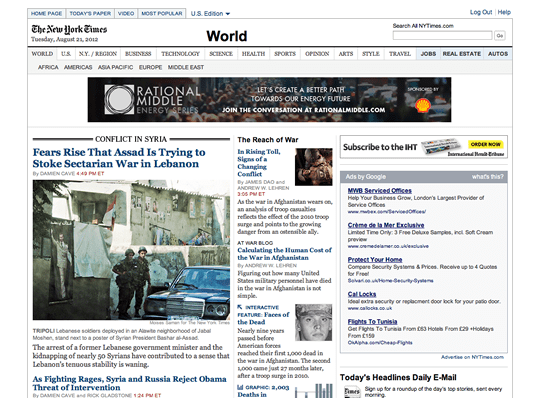
The inappropriateness of this design turns into extra obvious when in comparison with its Chrome App (which is fortunately accessible in different browsers). Content material takes middle stage, with a much less cluttered, extra centered interface that’s additionally responsive—to some extent. Word that it additionally options much less photographic imagery, supporting the concept that responsive pictures may solely be an issue when internet designers attempt to replicate print.

Job-oriented websites#section12
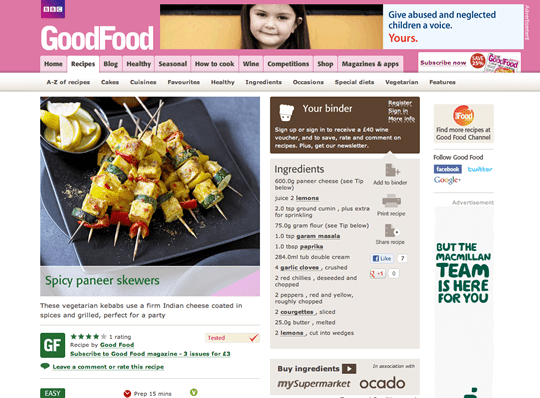
One other web site that suffers from equally crowded layouts is BBC Good Meals:
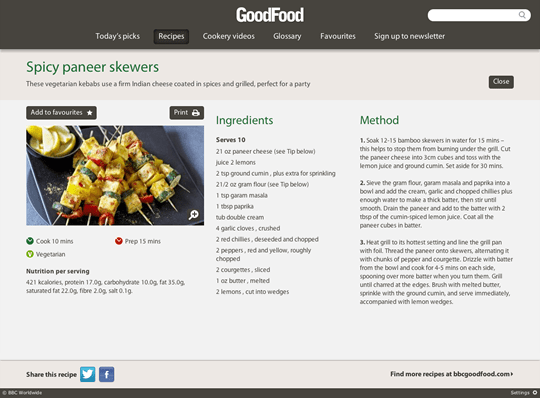
But, when viewing a recipe web page in its Chrome app, we once more see a extra thought of, user-centered design; it’s far simpler to comply with a recipe if you don’t need to scroll the web page.
Content material, not chrome#section13
A closing instance of this pattern may be discovered on Rdio. Because the music-streaming service has developed, its designers have sought consistency between the web site and desktop utility. The place as soon as these interfaces shared just a few parts, now they’re largely the identical. This has resulted in a design that falls someplace between the 2: not fairly a web site, however not fairly a desktop utility both.
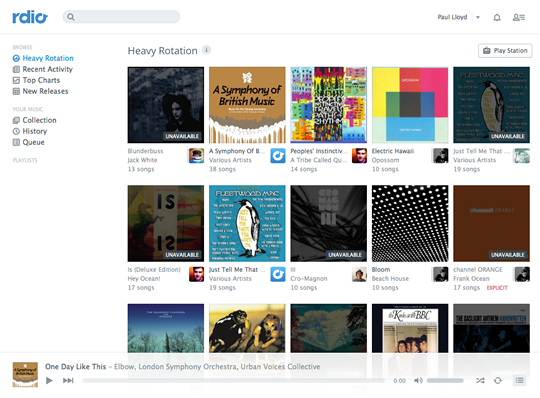
Just like the Chrome apps for The New York Occasions and BBC Good Meals, this nudge towards a extra app-like interface has resulted in a stronger deal with content material (on this case, album covers), a extra fluid structure, and fewer intrusive navigation.
In some respects, the brand new interface shares qualities with Microsoft’s “Metro” design language, discovered on Home windows Telephone and Home windows 8. When you think about that a number of the design rules behind Metro embrace “Clear, Mild, Open and Quick,” “Content material, Not Chrome,” and “Be Authentically Digital,” it could be onerous to argue that these values couldn’t equally apply to internet interfaces.
In fact, one of many causes these apps may be handled in another way from conventional web sites is the absence of show promoting—a constraint not a lot of the net, however of the enterprise fashions constructed upon it. Internet marketing is enduring an extended and painful demise: Adverts are getting bigger and extra hostile, whereas companies that take away them, like AdBlock, Instapaper, and Readability, are gaining reputation. But with out confirmed enterprise fashions to exchange it, show promoting will doubtless stick with us for a couple of extra years.
This shouldn’t cease us from studying from these app-inspired designs, although. On the very least, they spotlight different structure potentialities, and the way fascinating companies may be when better focus is given to content material.
The journey continues#section14
As we enter the third decade of the net’s existence, we ought to be gaining a way of what works, and what doesn’t. We should always now have the arrogance to decide on which facets of different media and platforms to take inspiration from, and which to disregard. We ought to be impressed by the conventions of different media, however now not ruled by them.
With universality as a tenet, we will ingrain approaches like progressive enhancement all through our design course of. Every part on the internet finally must degrade all the way down to plain textual content (pictures require alt textual content; movies require transcripts), so the textual content editor may simply grow to be probably the most highly effective app within the designer’s toolbox.
As the net matures, we should always acknowledge and embrace its constraints—and the aesthetic these constraints can produce. Once we do, we would uncover that the true internet aesthetic is hardly visible in any respect.