We’ve all seen arguments within the design group that dismiss the function of magnificence in visible interfaces, insisting that good designers base their selections strictly on issues of branding or fundamental design ideas. Misplaced in these discussions is an understanding of the highly effective function aesthetics play in shaping how we come to know, really feel, and reply.
Article Continues Beneath
Think about how designers “pores and skin” an info architect’s wireframes. Or how the time period “eye sweet” means that visible design is inessential. Our language constrains visible design to mere styling and separates aesthetics and value, as if they’re distinct concerns. But, if we shift the dialog away from graphical parts and as a substitute concentrate on aesthetics, or “the science of how issues are recognized by way of the senses,” we study that this distinction between how one thing appears and the way it works is considerably synthetic.
For starters, aesthetics is worried with something that appeals to the senses—not simply what we see, however what we hear, odor, style, and really feel. In brief, how we understand and interpret the world. As person expertise professionals, we should think about each stimulus which may affect interactions.
Maybe extra importantly, “aesthetics examines our affective area response to an object or phenomenon” (in keeping with Wikipedia). In different phrases, aesthetics is not only concerning the inventive benefit of internet buttons or different visible results, however about how folks reply to those parts. Our query turns into: how do aesthetic design selections affect understanding and feelings, and the way do understanding and feelings affect habits?
Aesthetics and cognition#section3
Cognition is “the method of figuring out.” Primarily based on patterns and experiences, we learn to perceive the world round us: What occurs if I push that? What does this shade recommend? Cognitive science research how folks know issues and aesthetics performs a essential function in cognitive processing. Within the instance under, which one among these is clearly a button? And why?

Right here, aesthetics communicates operate. The instance on the precise resembles a bodily button. The beveled edges and gradient shading take away any doubt about its operate. On this case, these are traits of affordance, that are points of design that assist a person to find how they may work together with an object. Translation: if it appears like a button, it have to be a button.
Equally, there’s a motive good confirmation screens have a examine mark and are more likely to contain some shade of inexperienced: Inexperienced is sweet. Crimson is dangerous. Yellow is one thing to consider. When designing, we should think about how our mind interprets the which means of shade, shadow, and shading. We not often discover these aesthetic selections, besides when folks get them flawed:

On this instance, the visible language confi‚icts with the intent of the message.
What we’re discussing right here is how our mind interprets the which means of issues resembling shade, shadow, shading, and different pure occurrences. Simply choose up a bit of paper and watch how the shadow modifications as you carry the web page nearer to you. It’s these sorts of pure occurrences our brains observe each day in the actual world. Once we use these cues on a display screen, they carry with them the identical actual world properties.
However, there’s extra to aesthetics than simply speaking operate, and extra to styling than mere enjoyment.
Aesthetics and have an effect on#section4
Once we discuss “have an effect on,” we’re speaking about emotions and feelings—not concerning the “I really feel constructive about your model” sense of emotions and feelings, however concerning the methods during which they affect perceived and precise usability. Let’s revisit our button instance, with a slight change:

Cognitively talking, each of those are clearly buttons. Neither button is “flawed” as in our earlier instance. Nevertheless, analysis into consideration, persuasion, alternative, happiness, studying, and different related matters means that the extra enticing button is more likely to be extra usable by most individuals. To get an concept of the place this attitude would possibly come from, think about this touch upon feelings from neurobiologist Antonio Damasio:
“…emotion just isn’t a luxurious: it’s an expression of fundamental mechanisms of life regulation developed in evolution, and is indispensable for survival. It performs a essential function in just about all points of studying, reasoning, and creativity. Considerably surprisingly, it might play a job within the building of consciousness.” [1]
In lots of design conversations, there’s a perception that functions are made gratifying as a result of we make them straightforward to make use of and environment friendly (apparently, whether or not it’s acknowledged or not, these conversations worth the function that aesthetics performs in cognition). Nevertheless, once we discuss how feelings affect interactions, it’s nearer to the reality to say issues which are gratifying might be straightforward to make use of and environment friendly. Enable me to elucidate.
You remind me of…#section5
Product character influences our perceptions. Take into consideration how shortly we type expectations about somebody merely primarily based on how they costume or current themselves. That is one thing the car trade has recognized for years, as they spend cash to create merchandise that categorical a specific character folks would possibly establish with. Why does a Dodge Ram appear extra sturdy? What makes a Mini Cooper appear zippy and enjoyable? Whereas there are actually efficiency options to help these psychological claims, we are able to additionally see these attributes expressed within the automobile’s type.
Equally, the UI design selections we make have an effect on the perceived character of our functions. Within the instance under, which window is friendlier? Which one appears extra skilled?
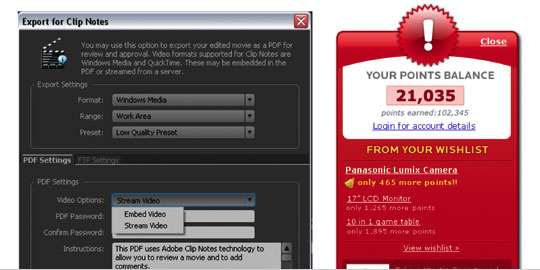
Merchandise have a character. Why ought to we care? Think about this:
- Folks establish with (or keep away from) sure personalities.
- Belief is said to character.
- Notion and expectations are linked with character.
- Customers “select” merchandise which are an extension of themselves.
- We deal with sufficiently superior expertise as if it have been human.
…and so forth.
By making intentional, acutely aware selections concerning the character of your product, you may form constructive or unfavourable responses. Check out Sony and the way they utilized this information within the Sony AIBO. Let’s think about why they made this robotic resemble a pet.
Right here, you may have a robotic gadget that isn’t excellent. It gained’t perceive most of what you say. It could or could not observe the instructions it does perceive. And it doesn’t actually do all that a lot.
If this robotic was an grownup butler that responded to solely half our requests and incessantly did one thing aside from what we requested, we’d think about it damaged and ineffective. However as a pet, we find its behaviors “cute.” Puppies aren’t recognized for following instructions. And when the robotic pet does succeed, we’re delighted. “Look, it rolled over!” What an effective way to enter the robotics market.
Think about: What sort of character are you creating together with your software? And what expectations does this character carry with it?
Are you able to belief me on this?#section6
In keeping with a 2002 examine, the “attraction of the general visible design of a website, together with structure, typography, font measurement, and shade schemes,” is the primary issue we use to guage a web site’s credibility.
This is smart. Take into consideration how our private look (our private aesthetic) impacts how folks understand us; or how product packaging infi‚uences our notion of the product inside.
Beneath is a gasoline pump close to my home. Distinction that with the station proven on the precise.

Picture (proper) by Sean Munson.
I’ve stopped filling up on the gasoline station on the left, regardless that it’s nearer to the place I dwell. Why? This sort of upkeep (or lack of upkeep) leaves me unwilling to belief them with my bank card info. Clearly, look does have an effect on belief.
So, how will we create belief in our software interfaces, except for offering the fundamentals, resembling dependable info and uptime? By taking note of visible design, for one factor. Consideration to design particulars implies that the identical care and a focus has been spent on the opposite (much less seen) elements of the product—which suggests that this can be a reliable product.
I’ve seen many nice design comps get butchered throughout growth. Issues resembling inconsistent fonts, odd padding, line-heights, and over-compressed photos plagued the final launch. Whereas this may increasingly by no means come out throughout useful testing, how would possibly these sloppy UI particulars have an effect on perceptions of your product?
Put all of it collectively and…#section7
Why ought to we actually care about perceptions? Think about these findings from analysis introduced at CHI 2007:
“…customers choose the relevancy of equivalent search outcomes from completely different search engines like google primarily based on the model…Contributors within the examine indicated that the outcomes from Google and Yahoo have been superior to equivalent outcomes discovered by Home windows Stay or a generic search engine.”
What’s a model however perceptions? On this examine, functionally equivalent outcomes have been perceived as higher as a result of model attributes resembling belief, character, and notion. What’s rational about that?
Maintain that thought.
Engaging issues work higher#section8
Okay, so perhaps perceptions are necessary to product design. However what about “actual” usability issues resembling decrease process completion instances or fewer difficulties? Do enticing merchandise truly work higher? This concept was examined in a examine carried out in 1995 (after which once more in 1997). Donald Norman describes it intimately in his guide Emotional Design.
Researchers in Japan setup two ATMs, “equivalent in operate, the variety of buttons, and the way they labored.” The one distinction was that one machine’s buttons and screens have been organized extra attractively than the opposite. In each Japan and Israel (the place this examine was repeated) researchers noticed that topics encountered fewer difficulties with the extra enticing machine. The enticing machine truly labored higher.
So now we’re left with this query: why did the extra enticing however in any other case equivalent ATM carry out higher?
Norman provides an evidence, citing evolutionary biology and what we find out about how our brains work. Principally, once we are relaxed, our brains are extra fi‚exible and extra more likely to find workarounds to difficult issues. In distinction, once we are annoyed and tense, our brains get a type of tunnel imaginative and prescient the place we solely see the issue in entrance of us. What number of instances, in a fit of frustration, have you ever tried the identical factor time and again, hoping it might by some means work the seventeenth time round?
One other rationalization: We wish these issues we find pleasing to succeed. We’re extra tolerant of issues with issues that we find enticing.
Stitching all of it collectively#section9
Current research into feelings are finding that we are able to’t truly separate cognition from have an effect on. Separate research in economics and in neuroscience are proving that:
“have an effect on, which is inexplicably linked to attitudes, expectations and motivations, performs a major function within the cognition of product interplay…the notion that have an effect on and cognition are impartial, separate info processing programs is flawed.” [2]
In different phrases, how we “assume” can’t be separated from how we “really feel.”

This raises some attention-grabbing questions—particularly within the space of determination making. In brief, our rational selections aren’t so rational. From research on option to first impressions, neuroscience is exploring how the mind works—and it’s form of scary. We’re not practically as accountable for our selections as we’d prefer to imagine.
Think about what you’re doing together with your interfaces to talk to folks’s feelings? Industrial product design, vehicle manufacturing and different extra mature industries get this—with instruments resembling Kano modeling which have been used for many years. However person interface growth continues to be maturing and catching as much as what these different disciplines already know: probably the most direct strategy to affect a call or notion is thru the feelings.
So, is “fairly design” necessary?#section10
Once we take into consideration software design and growth, how do you consider visible design? Is it a pores and skin, that provides some worth—a layer on high of the core performance? Or is that this magnificence one thing extra?
Within the early 1900s, “type follows operate” grew to become the mantra of recent structure. Frank Lloyd Wright modified this phrase to “type and performance ought to be one, joined in a religious union,” utilizing nature as the very best instance of this integration.
The extra we study folks, and the way our brains course of info, the extra we study the reality of that phrase: type and performance aren’t separate gadgets. If we imagine that type by some means exists impartial of performance, that we are able to deal with aesthetics and performance as two separate items, then we ignore the proof that magnificence is rather more than ornament. Our brains can’t assist however agree.
[] Emotion and Emotions: A Neurobiological Perspective by Ant³nio Dam¡sio [] “Emotion as a Cognitive Artifact and the Design Implications for Merchandise Which are Perceived As Pleasurable” by Frank Spillers