CSS is about styling containers. The truth is, the entire net is manufactured from containers, from the browser viewport to components on a web page. However each occasionally a brand new characteristic comes alongside that makes us rethink our design strategy.
Article Continues Under
Spherical shows, for instance, make it enjoyable to play with round clip areas. Cell display screen notches and digital keyboards supply challenges to greatest arrange content material that stays away from them. And twin display screen or foldable units make us rethink greatest use accessible house in various totally different machine postures.
These latest evolutions of the net platform made it each tougher and extra attention-grabbing to design merchandise. They’re nice alternatives for us to interrupt out of our rectangular containers.
I’d like to speak a couple of new characteristic just like the above: the Window Controls Overlay for Progressive Net Apps (PWAs).
Progressive Net Apps are blurring the traces between apps and web sites. They mix one of the best of each worlds. On one hand, they’re secure, linkable, searchable, and responsive similar to web sites. However, they supply further highly effective capabilities, work offline, and skim recordsdata similar to native apps.
As a design floor, PWAs are actually attention-grabbing as a result of they problem us to consider what mixing net and device-native consumer interfaces could be. On desktop units particularly, we now have greater than 40 years of historical past telling us what functions ought to appear to be, and it may be arduous to interrupt out of this psychological mannequin.
On the finish of the day although, PWAs on desktop are constrained to the window they seem in: a rectangle with a title bar on the prime.
Right here’s what a typical desktop PWA app appears to be like like:
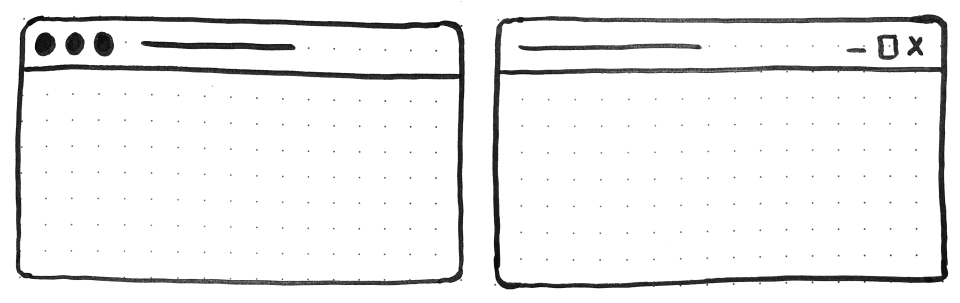
Positive, because the creator of a PWA, you get to decide on the colour of the title bar (utilizing the Net Utility Manifest theme_color property), however that’s about it.
What if we may assume exterior this field, and reclaim the true property of the app’s whole window? Doing so would give us an opportunity to make our apps extra lovely and really feel extra built-in within the working system.
That is precisely what the Window Controls Overlay affords. This new PWA performance makes it attainable to make the most of the total floor space of the app, together with the place the title bar usually seems.
In regards to the title bar and window controls#section2
Let’s begin with a proof of what the title bar and window controls are.
The title bar is the realm displayed on the prime of an app window, which normally comprises the app’s title. Window controls are the affordances, or buttons, that make it attainable to attenuate, maximize, or shut the app’s window, and are additionally displayed on the prime.
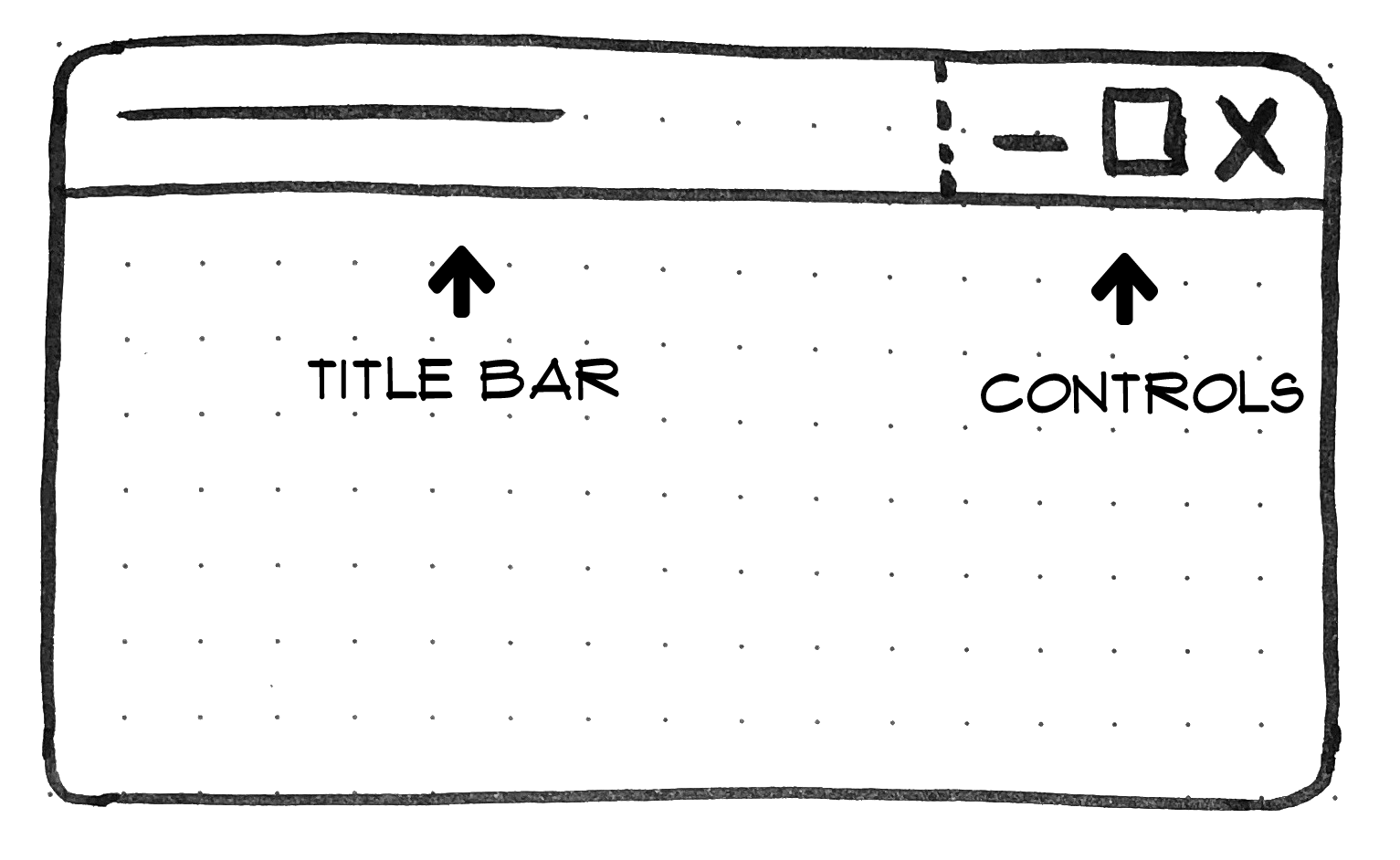
Window Controls Overlay removes the bodily constraint of the title bar and window controls areas. It frees up the total peak of the app window, enabling the title bar and window management buttons to be overlaid on prime of the appliance’s net content material.
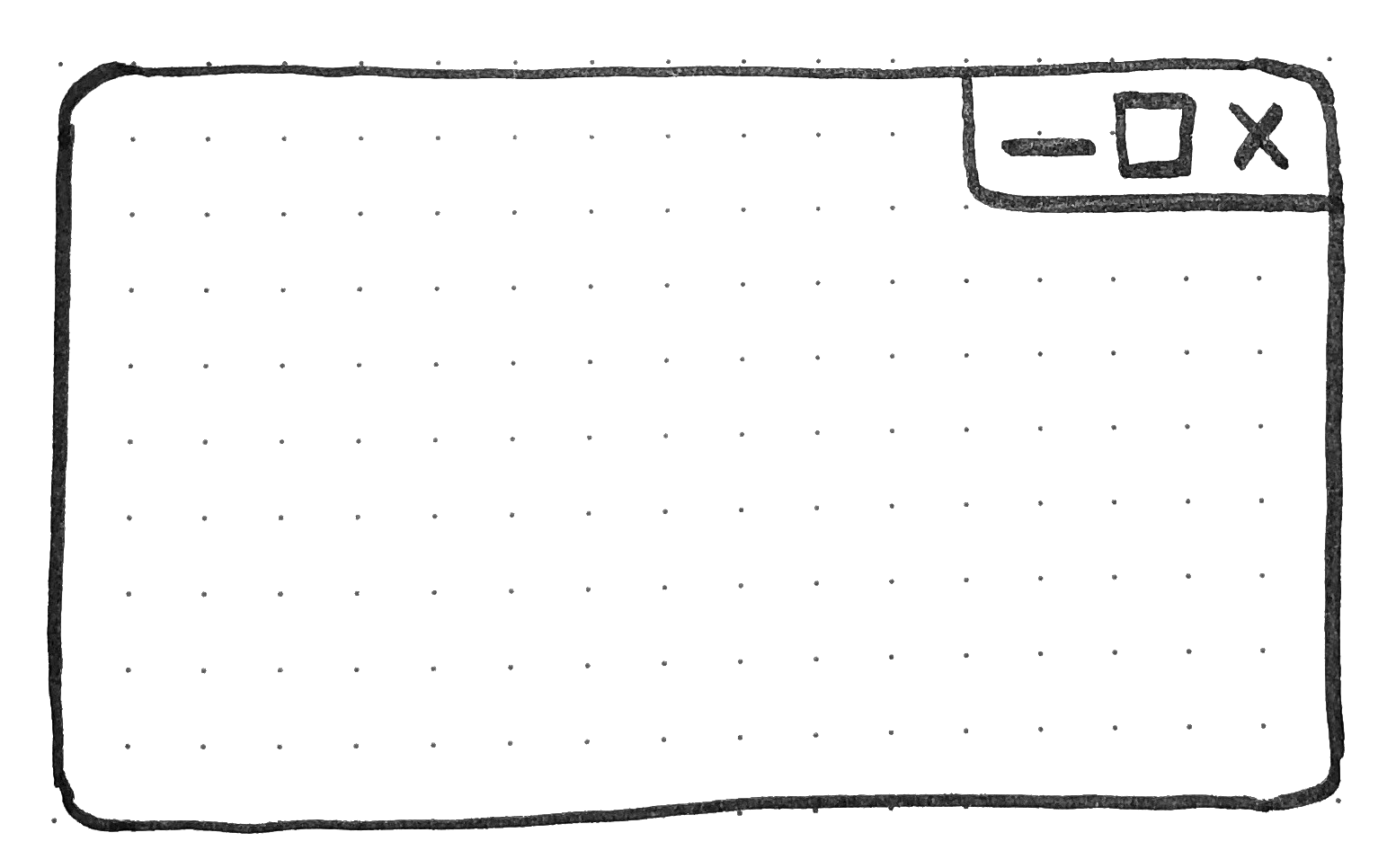
In case you are studying this text on a desktop pc, take a fast have a look at different apps. Chances are high they’re already doing one thing just like this. The truth is, the very net browser you’re utilizing to learn this makes use of the highest space to show tabs.
Spotify shows album art work all the way in which to the highest fringe of the appliance window.

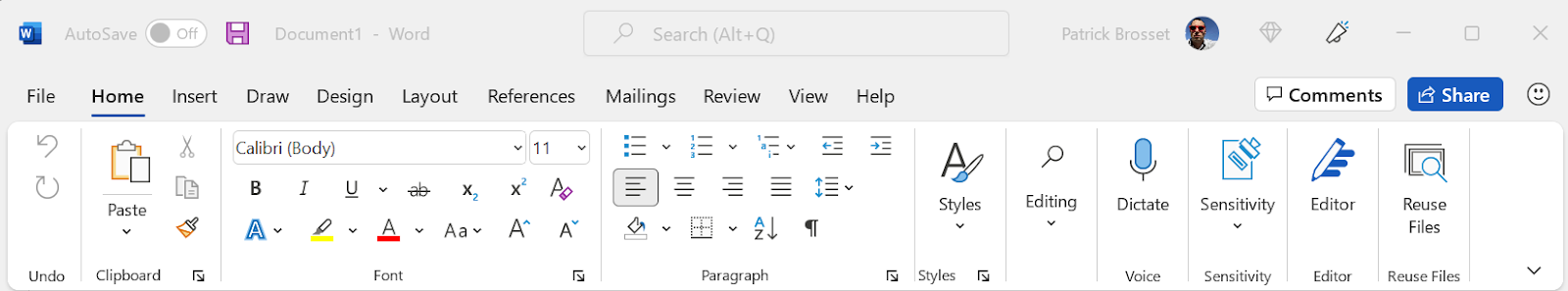
Microsoft Phrase makes use of the accessible title bar house to show the auto-save and search functionalities, and extra.
The entire level of this characteristic is to let you make use of this house with your individual content material whereas offering a approach to account for the window management buttons. And it lets you supply this modified expertise on a spread of platforms whereas not adversely affecting the expertise on browsers or units that don’t help Window Controls Overlay. In any case, PWAs are all about progressive enhancement, so this characteristic is an opportunity to boost your app to make use of this additional house when it’s accessible.
Let’s use the characteristic#section3
For the remainder of this text, we’ll be engaged on a demo app to be taught extra about utilizing the characteristic.
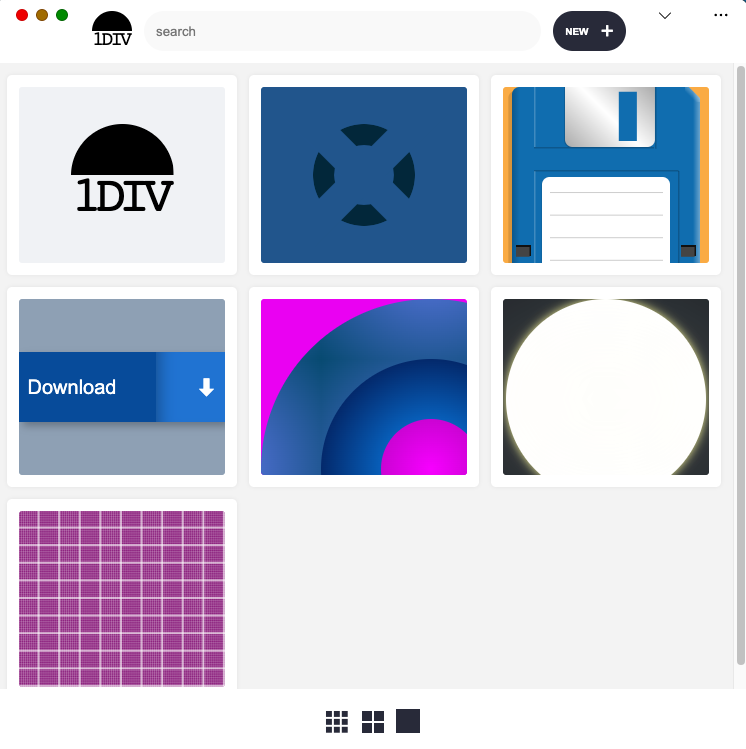
The demo app is known as 1DIV. It’s a easy CSS playground the place customers can create designs utilizing CSS and a single HTML component.
The app has two pages. The primary lists the prevailing CSS designs you’ve created:
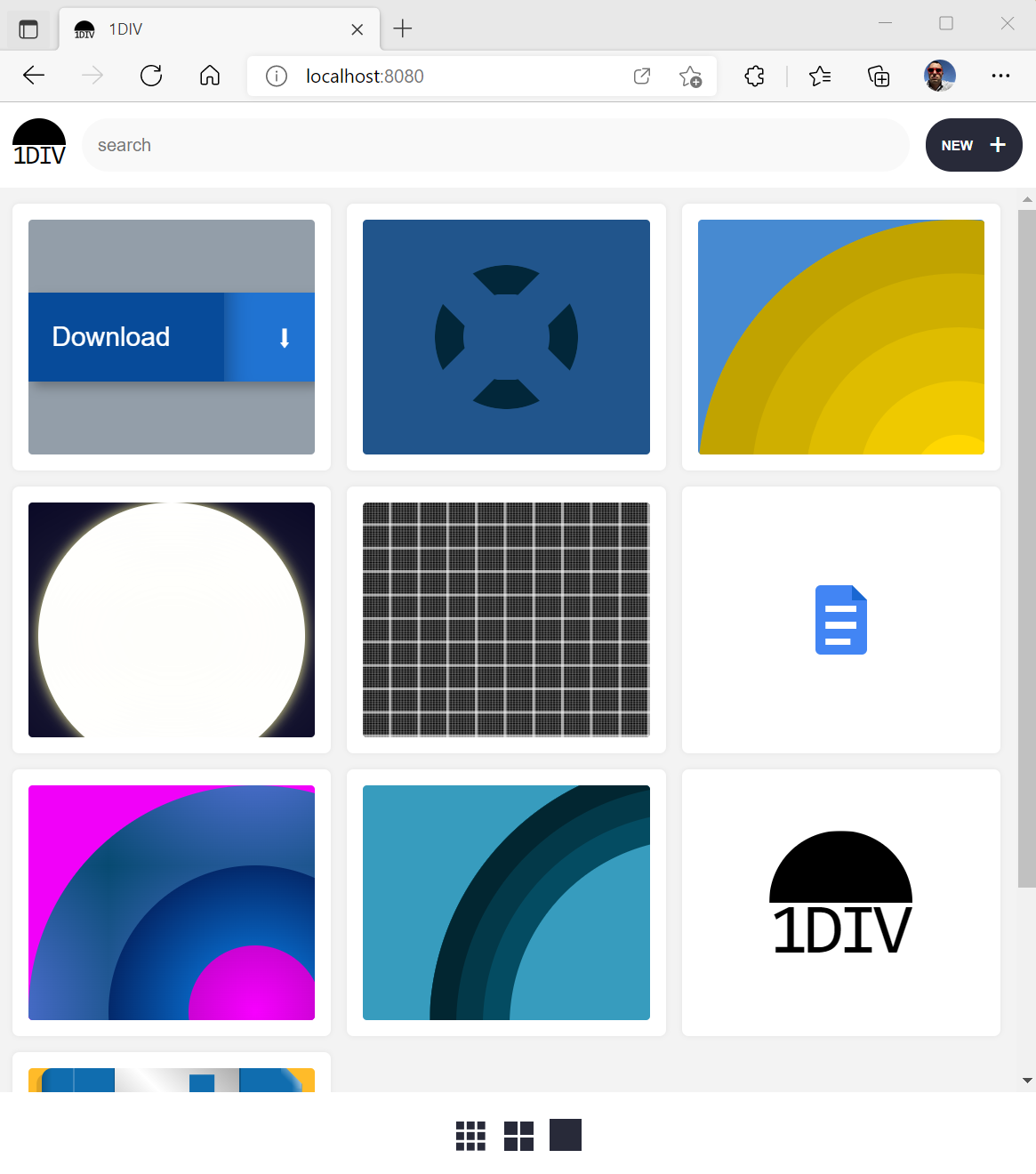
The second web page lets you create and edit CSS designs:
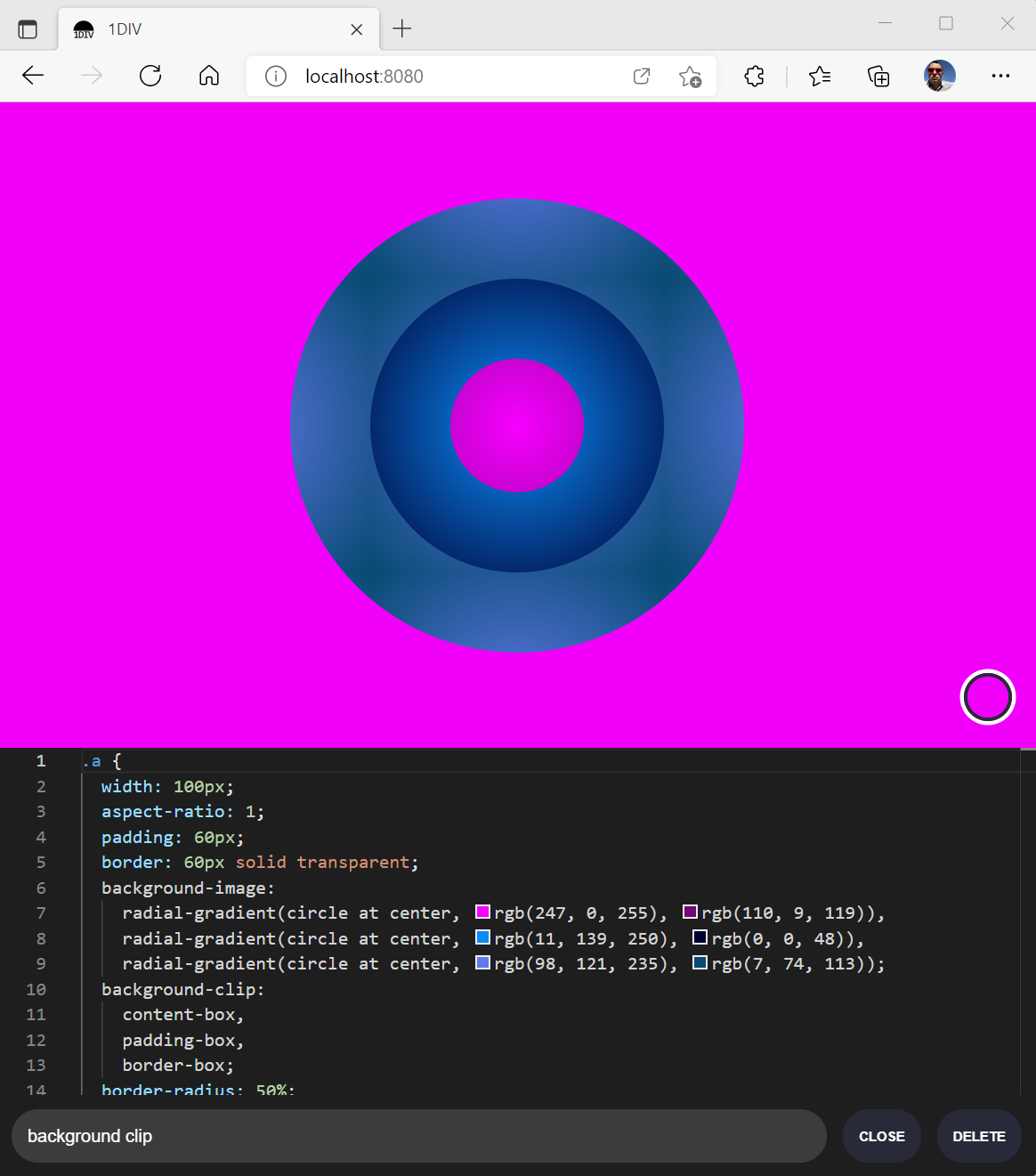
Since I’ve added a easy net manifest and repair employee, we are able to set up the app as a PWA on desktop. Here’s what it appears to be like like on macOS:
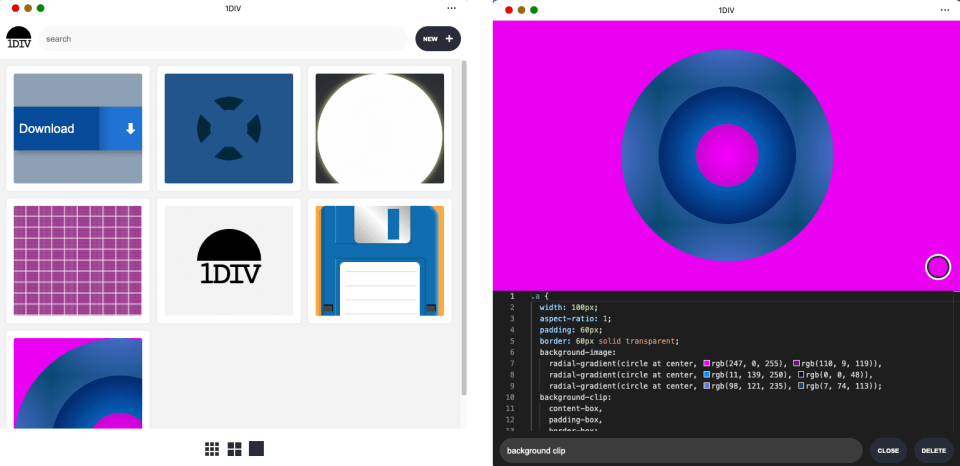
And on Home windows:
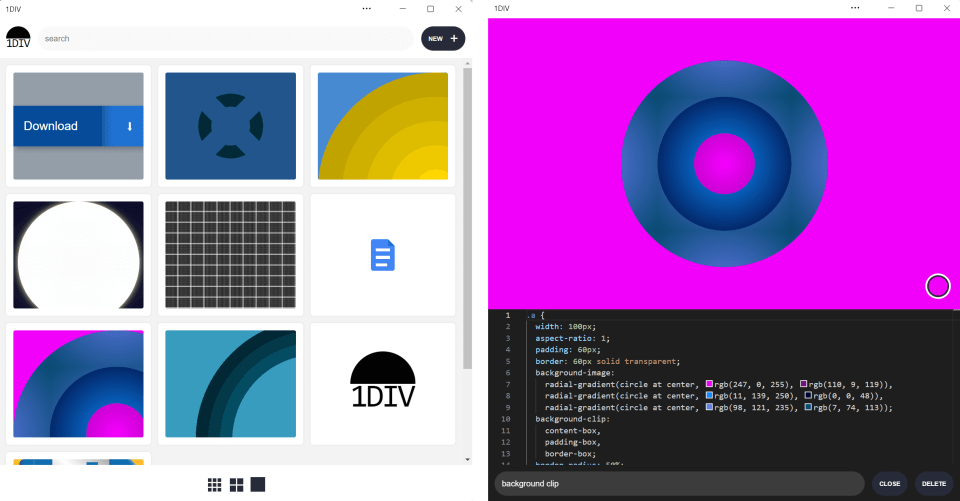
Our app is trying good, however the white title bar within the first web page is wasted house. Within the second web page, it will be very nice if the design space went all the way in which to the highest of the app window.
Let’s use the Window Controls Overlay characteristic to enhance this.
Enabling Window Controls Overlay#section4
The characteristic continues to be experimental in the mean time. To attempt it, it’s essential to allow it in one of many supported browsers.
As of now, it has been applied in Chromium, as a collaboration between Microsoft and Google. We are able to subsequently use it in Chrome or Edge by going to the interior about://flags web page, and enabling the Desktop PWA Window Controls Overlay flag.
Utilizing Window Controls Overlay#section5
To make use of the characteristic, we have to add the next display_override member to our net app’s manifest file:
{
"title": "1DIV",
"description": "1DIV is a mini CSS playground",
"lang": "en-US",
"start_url": "/",
"theme_color": "#ffffff",
"background_color": "#ffffff",
"display_override": [
"window-controls-overlay"
],
"icons": [
...
]
}
On the floor, the characteristic is basically easy to make use of. This manifest change is the one factor we have to make the title bar disappear and switch the window controls into an overlay.
Nonetheless, to supply a terrific expertise for all customers no matter what machine or browser they use, and to profit from the title bar space in our design, we’ll want a little bit of CSS and JavaScript code.
Here’s what the app appears to be like like now:

The title bar is gone, which is what we needed, however our brand, search area, and NEW button are partially coated by the window controls as a result of now our format begins on the prime of the window.
It’s comparable on Home windows, with the distinction that the shut, maximize, and reduce buttons seem on the best facet, grouped along with the PWA management buttons:
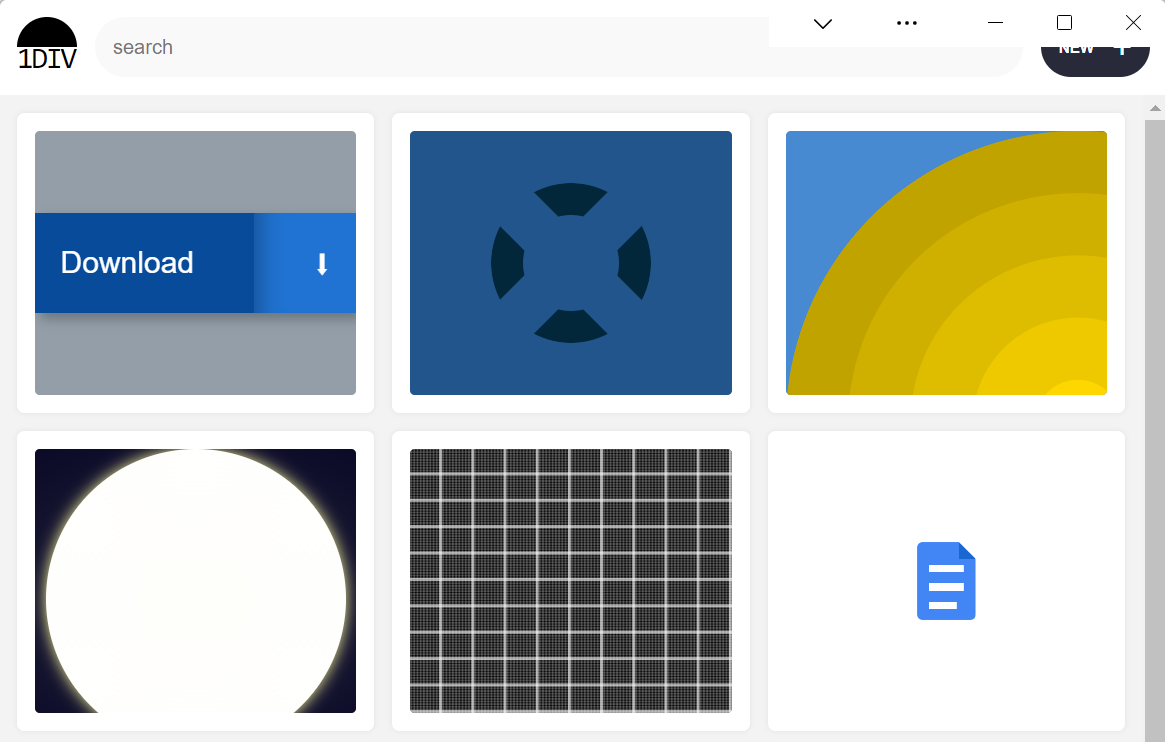
Utilizing CSS to maintain away from the window controls#section6
Together with the characteristic, new CSS atmosphere variables have been launched:
titlebar-area-xtitlebar-area-ytitlebar-area-widthtitlebar-area-height
You utilize these variables with the CSS env() perform to place your content material the place the title bar would have been whereas making certain it gained’t overlap with the window controls. In our case, we’ll use two of the variables to place our header, which comprises the emblem, search bar, and NEW button.
header {
place: absolute;
left: env(titlebar-area-x, 0);
width: env(titlebar-area-width, 100%);
peak: var(--toolbar-height);
}
The titlebar-area-x variable offers us the gap from the left of the viewport to the place the title bar would seem, and titlebar-area-width is its width. (Keep in mind, this isn’t equal to the width of the whole viewport, simply the title bar portion, which as famous earlier, doesn’t embody the window controls.)
By doing this, we be certain our content material stays absolutely seen. We’re additionally defining fallback values (the second parameter within the env() perform) for when the variables usually are not outlined (equivalent to on non-supporting browsers, or when the Home windows Management Overlay characteristic is disabled).
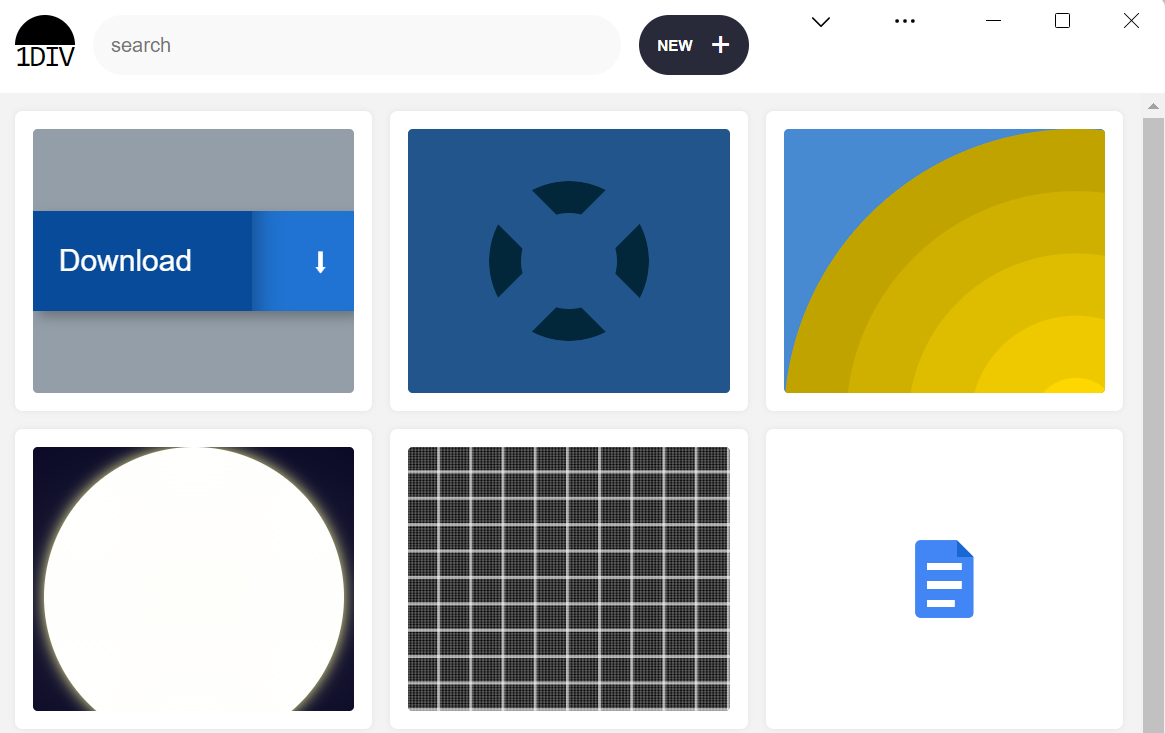
Now our header adapts to its environment, and it doesn’t really feel just like the window management buttons have been added as an afterthought. The app appears to be like much more like a local app.
Altering the window controls background colour so it blends in#section7
Now let’s take a more in-depth have a look at our second web page: the CSS playground editor.
Not nice. Our CSS demo space does go all the way in which to the highest, which is what we needed, however the way in which the window controls seem as white rectangles on prime of it’s fairly jarring.
We are able to repair this by altering the app’s theme colour. There are a few methods to outline it:
- PWAs can outline a theme colour within the net app manifest file utilizing the theme_color manifest member. This colour is then utilized by the OS in numerous methods. On desktop platforms, it’s used to supply a background colour to the title bar and window controls.
- Web sites can use the theme-color meta tag as effectively. It’s utilized by browsers to customise the colour of the UI across the net web page. For PWAs, this colour can override the manifest
theme_color.
In our case, we are able to set the manifest theme_color to white to supply the best default colour for our app. The OS will learn this colour worth when the app is put in and use it to make the window controls background colour white. This colour works nice for our predominant web page with the record of demos.
The theme-color meta tag could be modified at runtime, utilizing JavaScript. So we are able to do this to override the white with the best demo background colour when one is opened.
Right here is the perform we’ll use:
perform themeWindow(bgColor) {
doc.querySelector("meta[name=theme-color]").setAttribute('content material', bgColor);
}With this in place, we are able to think about how utilizing colour and CSS transitions can produce a clean change from the record web page to the demo web page, and allow the window management buttons to mix in with the remainder of the app’s interface.
Dragging the window#section8
Now, eliminating the title bar solely does have an necessary accessibility consequence: it’s far more tough to maneuver the appliance window round.
The title bar gives a large space for customers to click on and drag, however through the use of the Window Controls Overlay characteristic, this space turns into restricted to the place the management buttons are, and customers must very exactly purpose between these buttons to maneuver the window.
Luckily, this may be mounted utilizing CSS with the app-region property. This property is, for now, solely supported in Chromium-based browsers and desires the -webkit- vendor prefix.
To make any component of the app change into a dragging goal for the window, we are able to use the next:
-webkit-app-region: drag;
It’s also attainable to explicitly make a component non-draggable:
-webkit-app-region: no-drag;
These choices could be helpful for us. We are able to make the whole header a dragging goal, however make the search area and NEW button inside it non-draggable to allow them to nonetheless be used as regular.
Nonetheless, as a result of the editor web page doesn’t show the header, customers wouldn’t have the ability to drag the window whereas enhancing code. So let’s use a unique strategy. We’ll create one other component earlier than our header, additionally completely positioned, and devoted to dragging the window.
<div class="drag"></div>
<header>...</header>.drag {
place: absolute;
prime: 0;
width: 100%;
peak: env(titlebar-area-height, 0);
-webkit-app-region: drag;
}With the above code, we’re making the draggable space span the whole viewport width, and utilizing the titlebar-area-height variable to make it as tall as what the title bar would have been. This manner, our draggable space is aligned with the window management buttons as proven beneath.
And, now, to ensure our search area and button stay usable:
header .search,
header .new {
-webkit-app-region: no-drag;
}With the above code, customers can click on and drag the place the title bar was once. It’s an space that customers anticipate to have the ability to use to maneuver home windows on desktop, and we’re not breaking this expectation, which is nice.
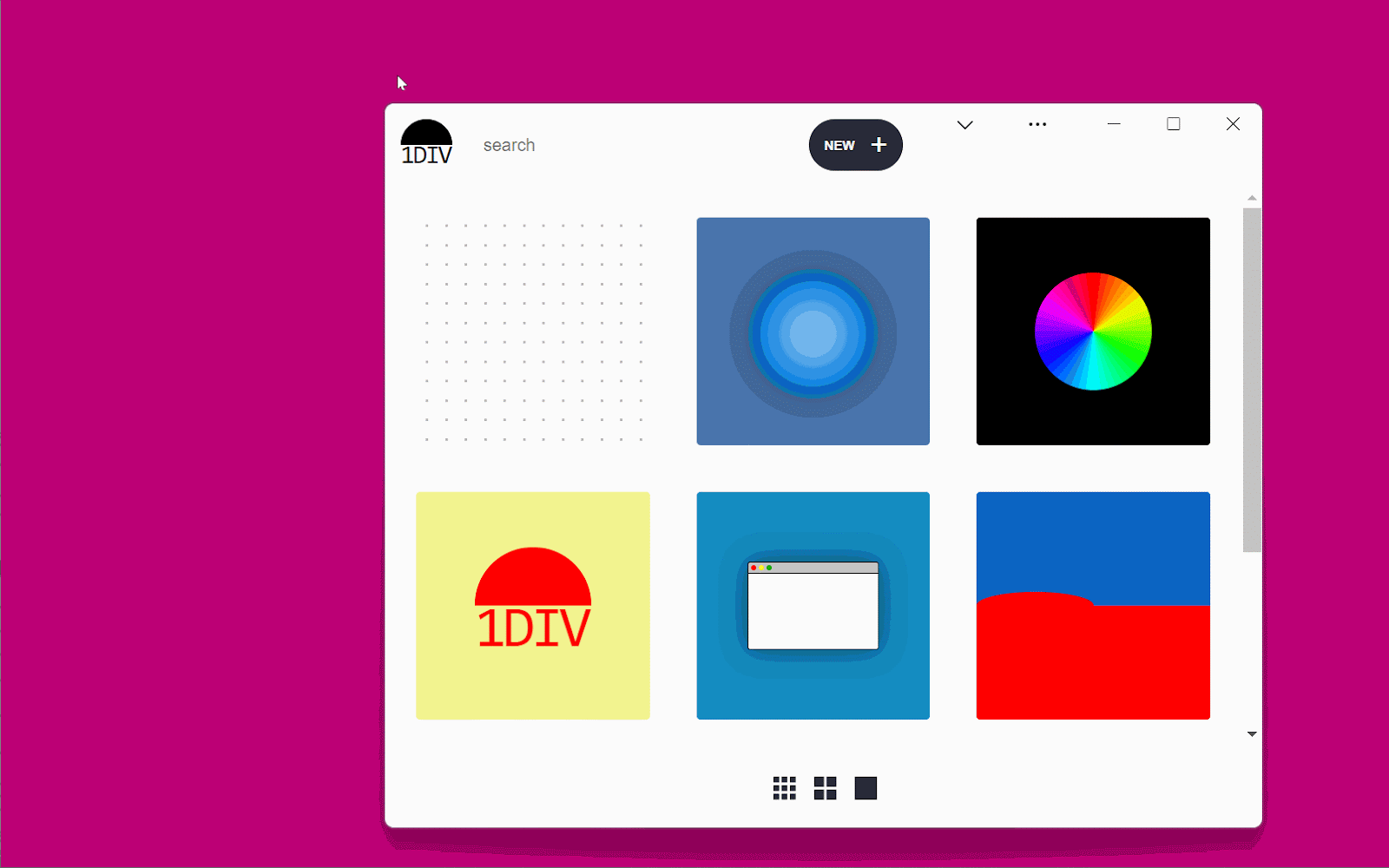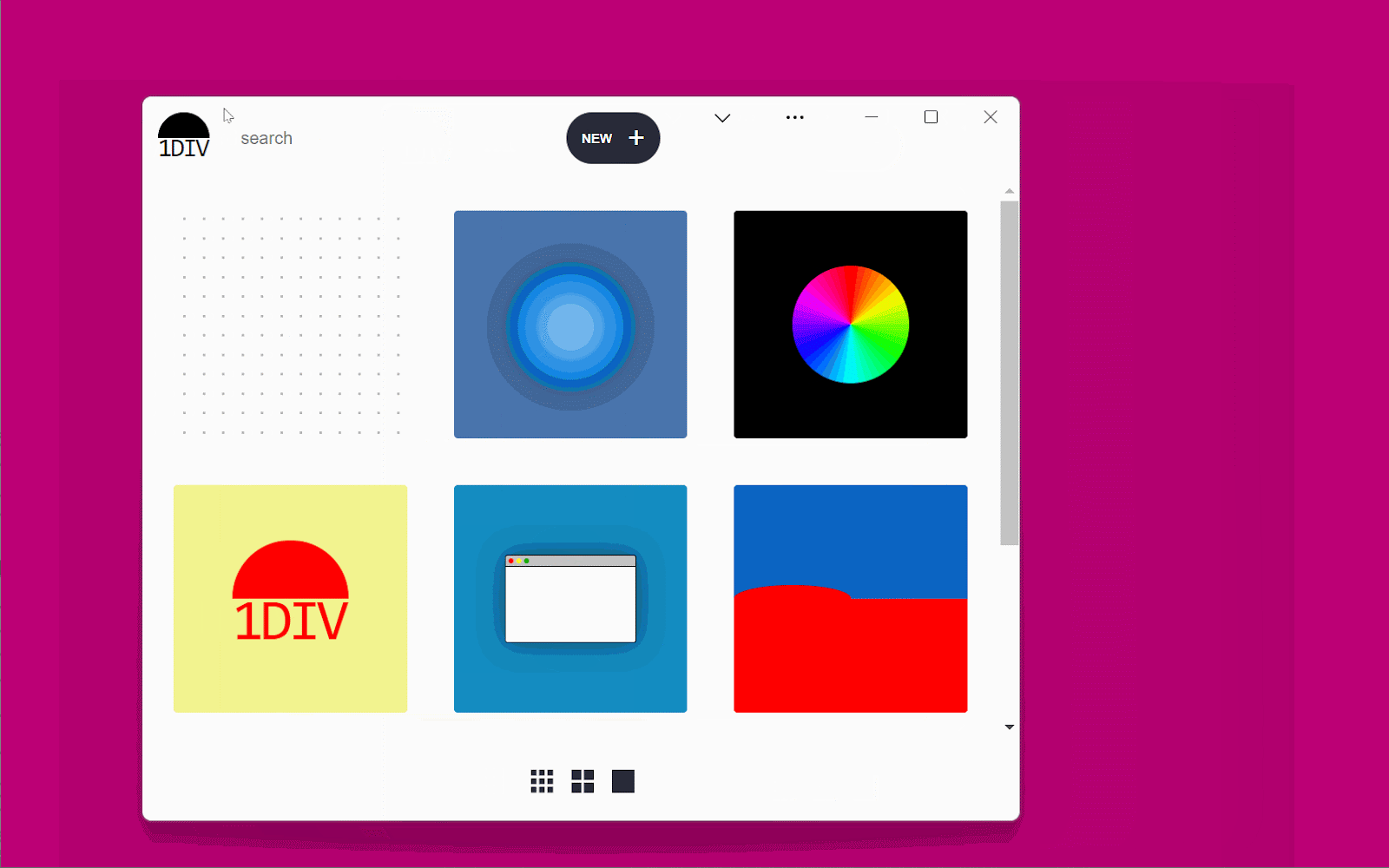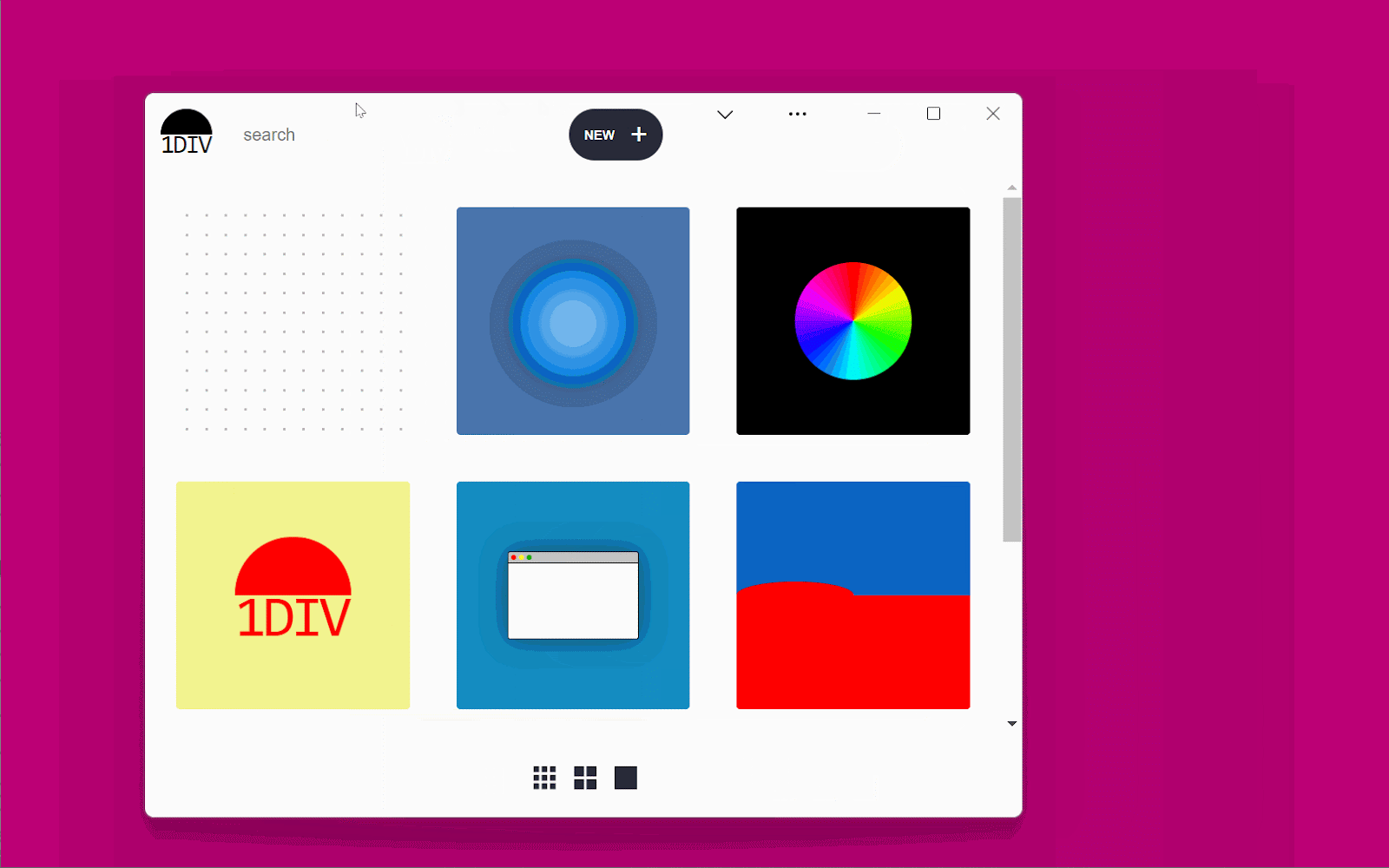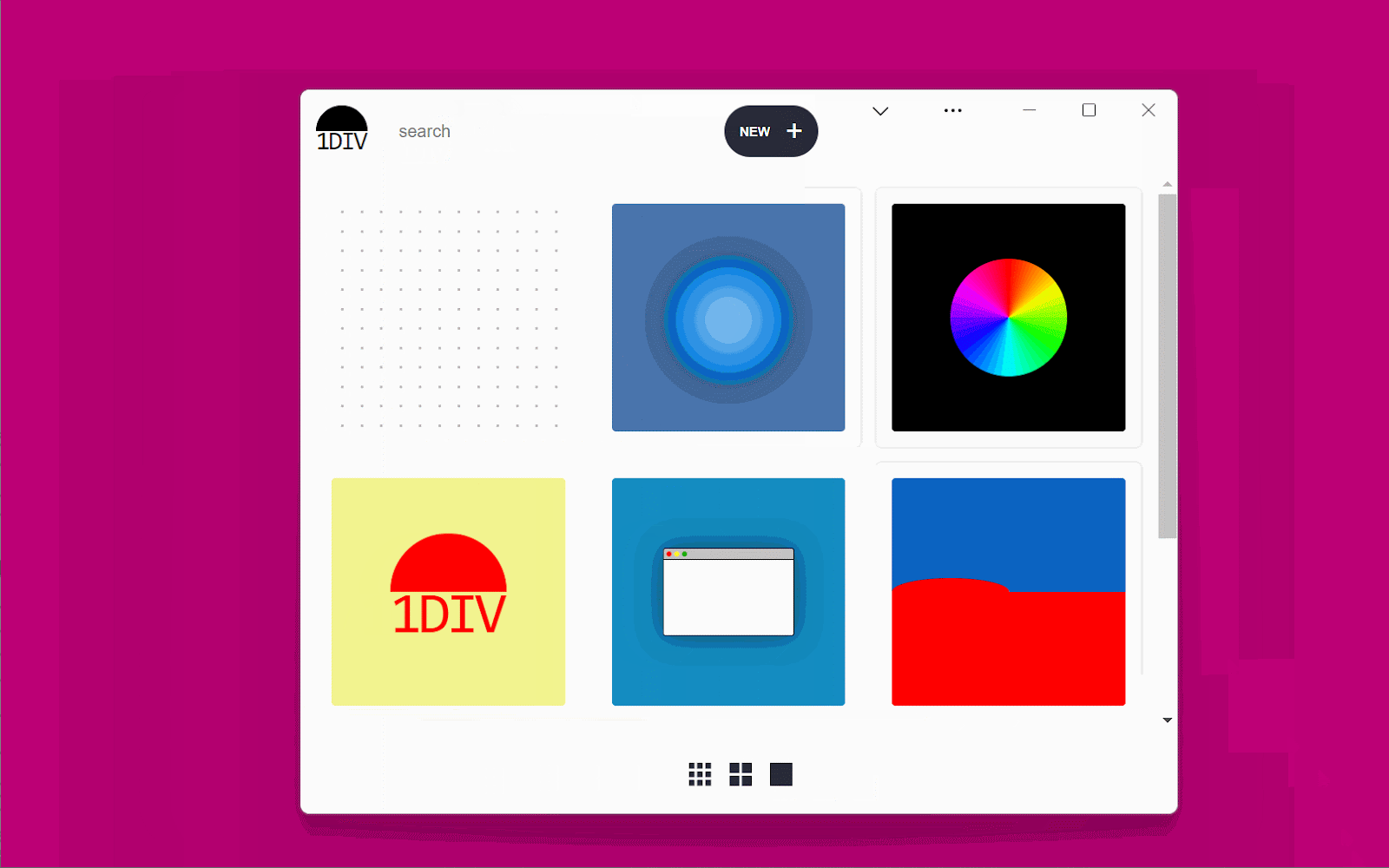
Adapting to window resize#section9
It could be helpful for an app to know each whether or not the window controls overlay is seen and when its measurement adjustments. In our case, if the consumer made the window very slender, there wouldn’t be sufficient house for the search area, brand, and button to suit, so we’d wish to push them down a bit.
The Window Controls Overlay characteristic comes with a JavaScript API we are able to use to do that: navigator.windowControlsOverlay.
The API gives three attention-grabbing issues:
navigator.windowControlsOverlay.seenlets us know whether or not the overlay is seen.navigator.windowControlsOverlay.getBoundingClientRect()lets us know the place and measurement of the title bar space.navigator.windowControlsOverlay.ongeometrychangelets us know when the dimensions or visibility adjustments.
Let’s use this to concentrate on the dimensions of the title bar space and transfer the header down if it’s too slender.
if (navigator.windowControlsOverlay) {
navigator.windowControlsOverlay.addEventListener('geometrychange', () => {
const { width } = navigator.windowControlsOverlay.getBoundingClientRect();
doc.physique.classList.toggle('slender', width < 250);
});
}Within the instance above, we set the slender class on the physique of the app if the title bar space is narrower than 250px. We may do one thing comparable with a media question, however utilizing the windowControlsOverlay API has two benefits for our use case:
- It’s solely fired when the characteristic is supported and used; we don’t wish to adapt the design in any other case.
- We get the dimensions of the title bar space throughout working methods, which is nice as a result of the dimensions of the window controls is totally different on Mac and Home windows. Utilizing a media question wouldn’t make it attainable for us to know precisely how a lot house stays.
.slender header {
prime: env(titlebar-area-height, 0);
left: 0;
width: 100%;
}Utilizing the above CSS code, we are able to transfer our header down to remain away from the window management buttons when the window is simply too slender, and transfer the thumbnails down accordingly.
Thirty pixels of thrilling design alternatives#section10
Utilizing the Window Controls Overlay characteristic, we have been in a position to take our easy demo app and switch it into one thing that feels a lot extra built-in on desktop units. One thing that reaches out of the same old window constraints and gives a customized expertise for its customers.
In actuality, this characteristic solely offers us about 30 pixels of additional room and comes with challenges on take care of the window controls. And but, this additional room and people challenges could be became thrilling design alternatives.
Extra units of all shapes and types get invented on a regular basis, and the net retains on evolving to adapt to them. New options get added to the net platform to permit us, net authors, to combine increasingly more deeply with these units. From watches or foldable units to desktop computer systems, we have to evolve our design strategy for the net. Constructing for the net now lets us assume exterior the oblong field.
So let’s embrace this. Let’s use the usual applied sciences already at our disposal, and experiment with new concepts to supply tailor-made experiences for all units, all from a single codebase!
In the event you get an opportunity to attempt the Window Controls Overlay characteristic and have suggestions about it, you may open points on the spec’s repository. It’s nonetheless early within the improvement of this characteristic, and you may assist make it even higher. Or, you may check out the characteristic’s current documentation, or this demo app and its supply code.