On this chapter, you’ll study these performs:
Article Continues Under
- Tips on how to create a jobs-driven roadmap
- Utilizing job tales to resolve particular design issues
- Tips on how to architect the construction of an answer
- Testing assumptions directed by JTBD
A software program firm I as soon as labored for held what have been known as “hackweeks” as soon as 1 / 4. This was a time for builders to work on “no matter they wished,” because it was framed. Give engineers time to mess around with know-how, and so they’re sure to search out the following innovation, or so the speculation went.
Hackweek was an enormous deal for us. Dozens of individuals organized it, and each developer within the firm stopped work to contribute to the hassle. It was expensive, however we have been dedicated to hackweek. In spite of everything, new software program choices come from new growth, proper?
Right here’s the way it went: small groups shaped to cobble collectively starter tasks representing using some new know-how. On the finish of the week, a panel judged the handfuls of ideas that emerged, and the successful “options” have been rewarded.
However in our case, hackweek was like capturing a shotgun within the incorrect path whereas blindfolded and hoping to hit the goal. The outcome was inevitably a group of ideas on the lookout for an issue to resolve. It was innovation theater at its finest.
To be truthful, not all hackathons are unhealthy. Some organizations coordinate hackathons with strategic imperatives or with buyer wants. And certain, it’s additionally good to flex artistic muscular tissues and observe collaboration throughout groups. However given their price and imprecision, hackathons are sometimes largely ineffective in producing usable ideas.
The issue isn’t a scarcity of concepts—corporations are often swimming in them. Like ours, many organizations have a Darwinistic outlook on innovation: generate increasingly more concepts, and one of the best will certainly rise to the highest. Stated one other approach, when on the lookout for a needle in a haystack, one of the best method isn’t so as to add extra hay.
The issue is figuring out which concepts to pursue. The purpose of innovation actions shouldn’t be to gather as many concepts as doable, however as a substitute to get to the correct concepts—those that matter most to the individuals you serve.
However greater than that, the true problem is in overcoming the pure forces in organizations that maintain good concepts down. Chief amongst these is uncertainty, a number one deterrent to innovation. New concepts are a bet for risk-averse managers, even when well-expressed in a high-fidelity prototype.
JTBD gives a approach to enhance your possibilities of success by first figuring out the correct drawback to resolve. Then JTBD provides you decision-making standards for transferring ahead: guess on options that deal with unmet must create worthwhile differentiation.
Focus first on getting the principle job achieved for the person and fulfilling their wants in relation to the job. From this angle, hackathons and different idea-generating efforts will be framed by JTBD as each inputs and outputs by way of how ideas are evaluated.
After understanding the job panorama and defining the worth you’re going after, you possibly can proceed utilizing JTBD considering to align groups across the design of your resolution. Create a roadmap primarily based in your JTBD panorama to set a standard path. Then use job tales to get everybody on the identical web page and tie native design efforts to the large image and to architect the answer construction. JTBD can even information the experiments you conduct to check your crew’s assumptions.
Create a Growth Roadmap#section2
At its highest degree, a roadmap is a sequence of growth occasions—the relative chronological order during which options and capabilities can be constructed. Roadmaps function a central level of reference for groups to align their efforts. They present the trail ahead with out defining particular person duties.
Within the age of Agile and Lean efforts, roadmaps have gotten a nasty popularity. Individuals are fast to level out—and rightfully so—that long-term plans inevitably fail: priorities change, unexpected challenges come up, and timelines slip. The answer, they could argue, is to don’t have any long-term plans and to work on brief initiatives with the flexibleness to alter as wanted.
However whereas offering decision-making energy to native growth groups is smart, total alignment remains to be wanted. Another approach of viewing roadmaps is to see them not as a definitive challenge plan, however as a imaginative and prescient of the way you’ll create an providing that clients will worth. Roadmaps should not unchanging predictions of future exercise, however a approach to offer transparency for the sequence of steps your crew will take to design options.
The knowledge in a roadmap helps the whole group get aligned, not simply builders. It’s a strategic communication software reflecting intention and path. Extra importantly, highway mapping isn’t simply concerning the artifact: it’s about getting a standard understanding of the place you’re headed. On this sense, the roadmap occupies the area between the imaginative and prescient and detailed challenge planning.
JTBD can assist create roadmaps that concentrate on the worth that the group intends to create and ship for purchasers. The trick is to get the correct drawback to resolve. Use the insights out of your JTBD investigation to formulate roadmaps which can be grounded in actual buyer want.
Mapping the Highway Forward#section3
For a concrete method to highway mapping, I like to recommend the ebook Product Roadmaps Relaunched by C. Todd Lombardo, Bruce McCarthy, Evan Ryan, and Michael Conners.[1] In it, the authors clearly articulate the steps to creating significant product roadmaps.
JTBD performs a key function in aligning to buyer wants, because the authors write: “We advocate beginning with the chunks of worth you propose to ship that can construct up over time to perform your visions. Usually it is a set of high-level buyer wants, issues, or jobs to be achieved.”
Their method breaks down the 4 key components of a superb product roadmap:
- Product imaginative and prescient: The imaginative and prescient outlines how your clients will profit out of your providing. How will the job performer profit from the answer? What is going to getting the job achieved appear like after the answer is in place?
- Enterprise aims: A roadmap have to be aligned with the group’s technique and aims. The objectives of the enterprise are essential for measuring progress.
- Timefames: Reasonably than committing to particular dates, good roadmaps sequence work and set broad timelines for completion.
- Themes: These are the important thing issues that clients face when finishing a job, or clusters of wants that align to the general resolution to be created. JTBD helps body the themes of your roadmap specifically.
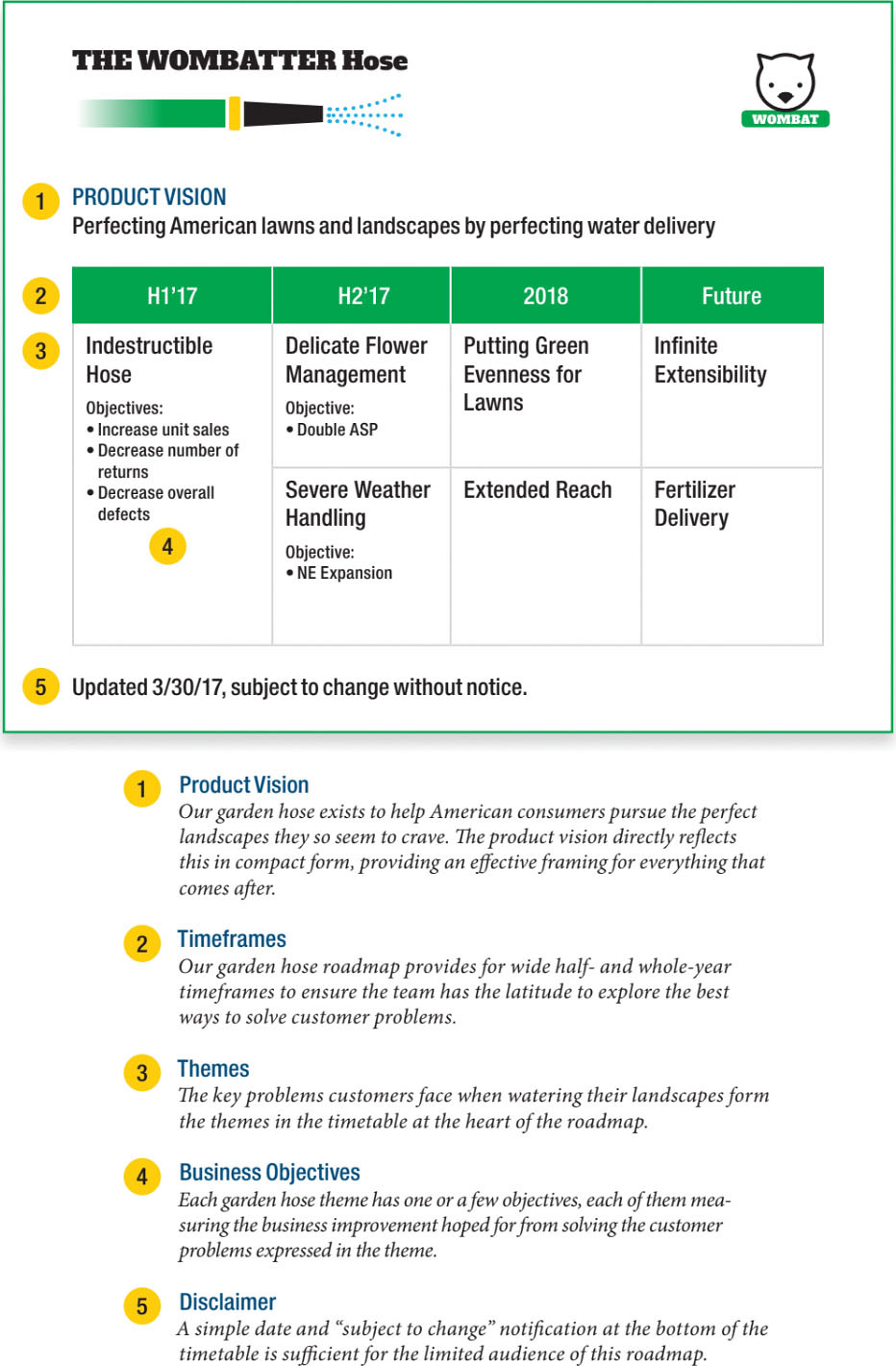
Determine 5.1 exhibits an instance from their ebook of a fundamental roadmap overview for a fictional firm, The Wombatter Hose, illustrating these important parts. Word the disclaimer, as properly, indicating that the roadmap is topic to alter.
Placing all of it collectively, the method for making a JTBD-driven roadmap will be damaged down into 4 phases.
Step 1: Outline the answer path.
Outline the assorted components of your total product technique to get settlement on the way you’ll be utilizing them. Along with your resolution imaginative and prescient, additionally outline the next along with the crew:
- Mission: What are your online business intentions? The mission is about what your group desires to in the end obtain.
- Values: What are your beliefs and beliefs? What’s the philosophy of your group and resolution? Values outline the philosophy of the crew and what it believes.
- Enterprise aims: What are the particular objectives your choices will accomplish for the group? Body these by way of outcomes, not outputs.
Step 2: Decide buyer must pursue.
Subsequent, resolve on the shopper must pursue. Right here, the authors of Product Roadmaps Relaunched stress the significance of grounding the roadmap in precise buyer want. JTBD is central to this step. They write:
“Figuring out buyer wants is crucial side of your roadmapping course of. Roadmaps needs to be about expressing these buyer wants. Due to this fact, most gadgets in your roadmap will derive from a job the shopper wants to perform or an issue the shopper should resolve.”
As outlined in Chapter 2, “Core Ideas of JTBD,” wants are hierarchical—from high-level aspirations to important jobs and sub-jobs to micro-jobs. Work out the top-level jobs to discover after which drill down into the particular themes to focus on.
The “worth themes,” as they’re known as, may come proper from the job map. Find the areas of highest underserved wants and use these levels because the classes of your roadmap themes. Or you possibly can cluster must type themes that don’t essentially comply with the chronology of the job map. The essential level is to floor the division of the roadmap in real-world observations of the shopper’s job to be achieved and align the timeline to it.
Step 3: Set a timeline.
Subsequent, create a sequence of worth themes that your crew will work towards. Timelines will be absolute, relative, or a mixture of each. Absolute timelines with particular dates carry the danger of fixing, which, in flip, could cause confusion or missed expectations.
Relative timelines give extra flexibility however nonetheless present perception into what’s coming and why. There are numerous phrases to make use of, however the timeline is usually damaged into three phases for near-term, mid-term, and long-term. Examples embody “now, later, future” or “going, subsequent, later” or one thing comparable. Discover what works finest for you.
Step 4: Align growth effort to the roadmap.
Lastly, conceptualize particular options to design and create. Use job tales to tie the general challenge intent to buyer wants, outlined within the subsequent part. Then conceptualize options round getting the whole job achieved or the elements of it decided to be most strategically related to your online business.
After a roadmap is created, it’s possible you’ll then want detailed challenge plans to trace progress. A easy Kanban board can serve that goal in lots of instances. Or, for extra complicated software program growth efforts, monitoring software program could also be wanted. In Agile efforts, epic planning after which dash planning come after you have got an total roadmap.
Tying the general plan to buyer wants provides the design and growth groups the sensation that they’re constructing one thing that issues to clients. Staying centered on buyer wants helps keep away from constructing issues your clients don’t need. The character of a job stays the identical, at the same time as options might shift. Grounding the roadmap in JTBD ensures that each its longevity and skill to soak up will change.
Be taught Extra About This Play#section4
Lombardo, C. Todd, Bruce McCarthy, Evan Ryan, and Michael Conners.[3] Product Roadmaps Relaunched. Sebastopol, CA:O’Reilly, 2018.
This ebook distills a wealth of sensible data right into a compact information on roadmapping. The authors go to nice lengths to offer quite a few examples and tales from real-world instances. They use a practical, trendy method for making a roadmap that’s pushed, partly, by JTBD.
Align Groups to Job Tales#section5
Agile growth permits groups and organizations to work in a versatile approach. The method began in software program growth, however has unfold to different domains, together with authorities and the army. The ideas of Agile growth can apply to simply about any discipline.
A key a part of Agile is to interrupt down efforts into particular person items of labor. Consumer tales are brief descriptions of options and performance written from the attitude of the top consumer. Groups can concentrate on solely a small a part of the entire and make progress in a managed approach.
Consumer tales are generally written in a three-part format. The primary factor signifies a consumer’s function within the system. The second factors to a functionality that permits the particular person to get a process achieved. The final half usually describes a profit or cause for utilizing the aptitude.
Though particular types can range, a typical consumer story resembles one thing like the next:
As a <function> I can <functionality>, in order that <profit>
Examples of use tales on this format embody:
- As a system admin, I can specify information or folders to again up primarily based on file measurement, date created, and date modified.
- As a consumer, I can point out folders to not again up in order that my drive isn’t crammed up with issues I don’t have to be saved.
- As a consumer, I wish to replace the identify of a doc in order that I can categorize it.
For any given system, there could also be a whole bunch of consumer tales. Some will be fairly granular, akin to describing a single button and why a consumer would click on it. Tales are then organized right into a backlog or repository of performance to be constructed. Groups break off logical teams of consumer tales in sprints or two- to four-week cycles of labor.
Job Tales#section6
Though consumer tales are good for breaking down work, they sometimes fail to attach the answer being constructed with consumer wants. They lack a sign of why somebody would behave in a sure approach and what they should get a job achieved. In actual fact, usually consumer tales are derived from the aptitude being constructed, not from observing precise habits.
Job tales are an alternative choice to consumer tales. They comply with the custom of breaking down efforts into smaller items, however by way of the JTBD lens. The approach was first pioneered by the product growth crew at Intercom, a number one advertising and marketing communications resolution. They wished to keep away from main designers with a preconceived resolution, in addition to tying growth to the corporate imaginative and prescient and technique.
Paul Adams, an Intercom product supervisor, wrote about job tales for the primary time, saying: “We body each design drawback in a Job, specializing in the triggering occasion or scenario, the motivation and purpose, and the supposed consequence.”[4]
Because of this, their job story format additionally has three elements. However as a substitute of specializing in a generic function, like a “consumer” or an “admin,” job tales start with a spotlight on the scenario and context, not the person:
When [situation], I wish to [motivation], so I can [expected outcome].
Examples of job tales embody:
- When an essential new buyer indicators up, I wish to be notified in order that I can begin a dialog with that particular person.
- Once I go to somebody’s profile web page, I wish to see what number of posts they’ve in every subject in order that I’ve an understanding of the place they’ve probably the most information.
- When I’ve used the applying a number of instances, I get nudged to contribute in order that I’m inspired to take part.
JTBD writer and chief Alan Klement has achieved probably the most work refining the job story format.[5] He believes that including extra details about the circumstances exhibits causality higher. Specializing in the context shifts consideration from a persona to the scenario. Klement advises that you just keep away from writing imprecise conditions, however as a substitute be as particular as doable.
For example, contemplate these three doable conditions for the primary factor of job tales:
- Once I’m hungry…
- Once I’m misplaced…
- Once I wish to verify my electronic mail…
As a substitute, Klement recommends describing the circumstances in wealthy element:
- Once I’m hungry, working late to get someplace, unsure after I’m going to eat once more, and frightened that I’ll quickly be drained and irritable from starvation…
- Once I’m misplaced in a metropolis that I’ve by no means been to, don’t know the native language, and am frightened that I’ll be losing my time in locations I don’t wish to be in…
- Once I wish to verify my electronic mail, however don’t need anybody round me to know I’m checking my electronic mail as a result of they’ll suppose I’m being impolite…
Every of those instance conditions gives extra context for designing an acceptable resolution.
Working with Job Tales#section7
Job tales are modular, giving designers and builders the flexibleness to resolve issues in other ways. Job tales are grounded in real-world perception, and they’re extra highly effective than consumer tales in guiding options. However creating job tales is extra free-form than different JTBD methods. Nonetheless, there are patterns which you can comply with. Utilizing the weather from Chapter 2, I recommend the next construction for job tales:
Once I [circumstance + job stage/step], I wish to [micro-job], so I can [need].
Examples:
- When I’m one of many prime posters whereas updating my social media feeds each day, I need it to point out on my profile in order that I can enhance recognition as an skilled on the topic.
- Once I run out of supplies wanted whereas finishing an artwork challenge, I wish to discover different supplies in order that I can maximize the variety of makes use of of my present provides.
- When making ready for my commute and working late, I wish to know the present climate alongside my journey in order that I can decrease the possibility of arriving moist.
Contemplate the final instance. The primary factor combines details about the circumstances (working late) of getting the principle job achieved (commute to work) inside a stage of the method (put together for commute).
The second factor factors to a good smaller step or micro-job (verify forecast). It needs to be formulated irrespective of particular know-how, however needs to be particular sufficient for designers and builders to create a selected functionality.
Lastly, the final factor will be taken proper out of your record of wants. On this case, the job performer (commuter) desires to keep away from exhibiting as much as the workplace moist (decrease the possibility of arriving at work moist). You possibly can leverage the weather your JTBD panorama already uncovered in analysis immediately within the formulation of the job story statements.
In researching this ebook, I’ve come throughout varied different approaches to formulating job tales. Andrea Hill, a outstanding advocate of JTBD on social media, suggests a barely completely different method. She sees the center factor pointing on to a characteristic or resolution of some form, thus explicitly crossing from the issue area into the answer area. Her fundamental format is as follows:
Once I [circumstance], I wish to [solution capability], so I can [need].
A job story for the earlier instance of commuting to work may then appear like this:
Once I’m making ready to commute to work, I wish to have climate forecast notifications pushed to my cellphone, so I can decrease the possibility of arriving moist.
Steph Troeph, analysis and JTBD teacher within the UK, approaches job tales in one more approach. She thinks of them with this components:
Once I [circumstance], I wish to [job], in order that [benefit a solution offers].
No matter your interpretation, the secret’s to discover a constant construction and keep it up. The shape you find yourself with must be acceptable to your crew and your scenario.
Jobs Tales in Motion#section8
Finally, job tales tie an area design and growth effort to a broader JTBD framework. As a result of the format of job tales consists of contextual particulars, they’re moveable. In different phrases, a job story ought to make sense with out having to know the bigger JTBD panorama or job map. Because of this, job tales have a extra “plug-and-play” versatility that’s usually required for Agile designs and growth groups.
For example, Agile planners can handle a backlog of job tales a lot in the identical approach that they might handle consumer tales. If a given dash will get slowed down or adjustments path, tales not addressed will be carried over to the following dash. Having a smaller, self-contained description of the smaller job to be achieved has benefits throughout the design and growth phases.
However to be clear: I’ve discovered that job tales sometimes don’t exchange consumer tales for growth fully. As a substitute, job tales information and body the conceptualization of an answer slightly than observe implementation. They serve finest as a design software to create or decide idea path and design. Builders and engineers will seemingly nonetheless want consumer tales to measure the burndown fee and total progress.
Your job map gives an total orientation to your JTBD panorama and means that you can zero in on a selected space for design and growth. A roadmap provides you a high-level sequence of growth with the rationale for planning actions. Job tales are extra particular and information the native design and growth of options and capabilities.
Comply with these steps to create job tales primarily based in your JTBD analysis:
Step 1: Perceive job levels and circumstances.
Base the related jobs and circumstances on earlier interviews and observations. For every space of growth in your resolution, contemplate the steps in the principle job. Then drill down and record the smaller and smaller steps as micro-jobs, utilizing the principles of formulating JTBD. Additionally establish the circumstances that apply to that a part of the principle job specifically.
Relying on the depth of your prior analysis and the way properly you and your crew perceive the job, it’s possible you’ll not have to do extra analysis to create and validate job tales. It’s by no means a nasty thought to talk with individuals once more and drill down on particular issues and aims they’ve. Throughout extra interviews, ask “how?” till you get extra granular in understanding of subgoals and aims.
Step 2: Formulate job tales.
As a crew, write job tales which can be particular to your design and growth effort. Resolve on a constant format for the job tales and follow it.
Attempt to give you distinctive, mutually unique tales that focus on particular jobs and circumstances. Keep away from redundancy. For example, within the earlier instance, you most likely don’t want separate tales for commuting by practice versus commuting by automotive. Develop the job tales that matter probably the most and concentrate on a restricted set. You might find yourself with anyplace from three to eight job tales per challenge or dash.
Step 3: Clear up for the job tales.
Make job tales seen and clear to the whole crew to resolve for the job tales. For example, submit a related record of job tales in a brainstorming session for everybody to see. Or record job tales initially of a design critique in order that the crew has context for making feedback. Use JTBD to information design and growth choices.
It’s additionally doable to then use the job tales to evaluate the appropriateness of your options. First, the design crew can use the job tales related to a challenge as heuristics. They need to always ask if their designs are assembly the consumer’s objectives set out within the job tales.
Then you possibly can take a look at options with customers towards the job tales. Present customers your options (e.g., as a mock-up or prototype) and ask them how properly every addresses the job tales. This may be achieved in an interview-style vogue or with a survey. The job tales in the end turn into a measure for fulfillment of the designs earlier than something is constructed.
Job tales allow you to take a step again and take a look at the context of the job whereas designing a services or products. On this respect, job tales fill an essential hole between the observations of consumers and resolution growth, connecting insights into buyer must particular person options and growth efforts.
Associated Approaches: Wants Statements#section9
Design considering is a broad framework for artistic drawback fixing. It’s rooted in human-centered strategies that search to develop deep empathy for individuals after which to plot options that meet their wants. In design considering, it is very important outline the issue to resolve earlier than producing choices for options.
One approach to encapsulate insights from analysis is to generate want statements, drastically resembling job tales in type. However these statements differ from “wants,” as outlined in Chapter 2, in that want statements in design considering should not particularly restricted to the outcomes of a getting a important job achieved, and they are often aspirational in nature.
Want statements in design considering additionally are typically way more centered on a persona or a person slightly than the circumstances. For example, writing for the Norman Nielsen Group, Sarah Gibbons refers to want statements representing a point-of-view for the consumer of a system:[6] “A consumer want assertion is an actionable drawback assertion used to summarize who a selected consumer is, the consumer’s want, and why the necessity is essential to that consumer.”
Like job tales, want statements have three parts: a consumer, a necessity, and a purpose. The consumer corresponds to a goal-based persona primarily based on analysis (as outlined in Chapter 4, “Defining Worth”). A want is expressed unbiased of a characteristic or know-how. The purpose is the results of assembly the necessity. Gibbons gives an instance:
Alieda, a multitasking, tech-savvy mom of two, must rapidly and confidently evaluate choices with out leaving her consolation zone in an effort to spend extra time doing the issues that actually matter.
Word that the perception on the finish of this assertion, “doing the issues that actually matter,” could be very broad and laborious to measure. Job tales, however, favor a extra particular context and consequence. For example, rewriting the above instance by way of the lens of job tales may yield one thing like the next:
Once I’m multitasking and in a rush, I would like a well-known approach to rapidly and confidently evaluate choices in order that I can decrease the time spent on discovering an answer.
Like want statements in design considering, job tales additionally keep away from the point out of options or know-how. But, they’re much extra particular to a given job and its context. Whereas each a necessity assertion from design considering and a job story can feed into the artistic era of options, job tales will present extra direct steering with out prescribing an answer.
However the definition of a want in design considering can range drastically. For example, IBM’s Enterprise Design Considering method additionally consists of tips for producing statements.[7] Not surprisingly, there are three elements: a consumer, a necessity, and a profit. Right here’s an instance from the IBM web site:
A developer wants a approach to make sense of minimal design in order that they’ll prototype quicker.
This instance is way more particular than Gibbon’s method, but nonetheless avoids mentioning a selected resolution. There are not any aspirational components, akin to “pursuing lifelong goals,” generally discovered elsewhere in design considering. IBM’s method to want statements is nearer to the job story method, however can also be mild on describing the circumstances of use.
In some sense, the variations between job tales—even with the variations in format—and wish statements factors to a key distinction between JTBD and design considering. The previous focuses way more on the circumstances than the particular person’s mind-set or psychology. The place design considering seeks to realize empathy for the person as a place to begin, JTBD seeks to grasp the circumstances of engaging in an goal earlier than factoring in emotional and private facets.
Be taught Extra About This Play#section10
Klement, Alan. “Changing the Consumer Story with the Job Story.” JTBD.information (2013); “5 Ideas for Writing a Job Story,” JTBD.information (2013); “Designing Options Utilizing Job Tales,” Inside Intercom (2015).
Klement has achieved probably the most in depth work to develop the job story approach. These three articles define the premise for creating them. The approach has developed barely, however Klement factors clearly to how he’s up to date his method. Klement and others have posted broadly about their use for growth efforts, however begin with these assets.
van de Keuken, Maxim. “Utilizing Job Tales and Jobs-to-be-Carried out in Software program Necessities Engineering.” Thesis, Utrecht College, 2017.
This thesis challenge affords an in depth investigation of how job tales are utilized so far. After illustrating the historical past of job tales, Van de Keuken presents the outcomes of his unique analysis variations in utility of job tales as seen in observe. This work contributes drastically to creating job tales a extra formal a part of software program necessities engineering.